Fig. 7.
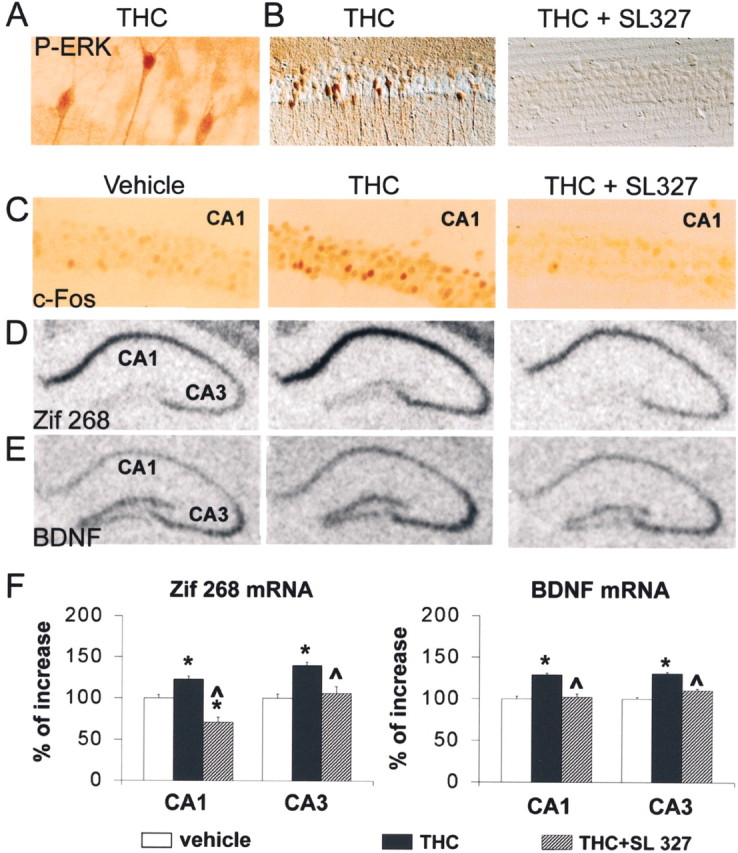
ERK-dependent induction of immediate-early genes by THC in hippocampus in vivo. A, Mice were injected with 1 mg/kg THC 10 min before they were killed, as in Figure 6A, High magnification of a peroxidase-labeled section shows the nuclear staining for dually phosphorylated ERK. B, The effects of THC (middle panel) were prevented in the CA1 region of mice injected with SL327 (100 mg/kg) 60 min before THC (right panel). Results shown are representative of four to six animals for each group. C, c-Fos immunoreactivity (peroxidase reaction) was examined in CA1 of mice injected with either vehicle (Veh) or 1 mg/kg THC 60 min before they were killed. SL327 (100 mg/kg) was injected 60 min before THC.D, Zif268 mRNA expression was analyzed by in situ hybridization in mouse hippocampus 1 hr after injection of vehicle, THC (1 mg/kg, i.p.), or THC and SL327 (100 mg/kg, 60 min before THC). Note the increased hybridization signals in the CA1 and CA3 regions. E, BDNF mRNA expression was analyzed byin situ hybridization in mouse hippocampus 1 hr after injection of vehicle, THC (1 mg/kg, i.p.), or THC and SL327 (100 mg/kg, 60 min before THC). F, Signals for mRNA hybridization were quantified using an image analyzer for six animals for each treatment. Statistical analyses used one-way ANOVA followed by apost hoc comparison with Newman–Keuls test; *p < 0.001 when comparing THC-treated mice with control mice; ^ p < 0.001 when comparing SL + THC with THC alone (n = 6 mice per group).
