Fig. 6.
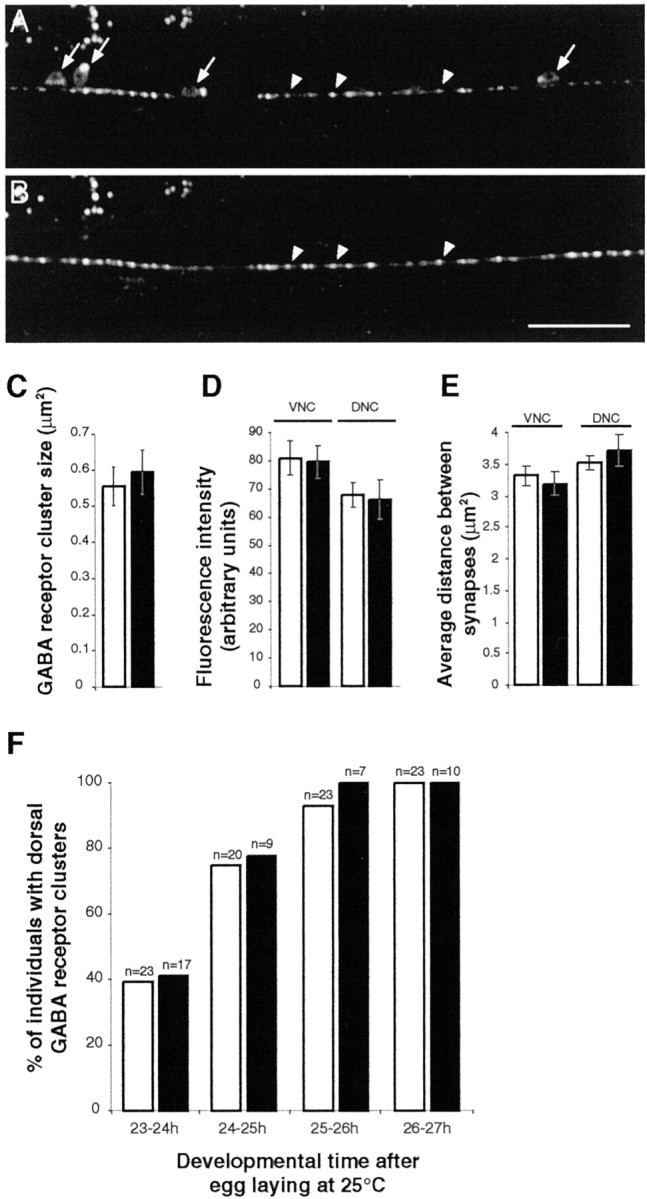
UNC-49 GABA receptor clustering is normal in the absence of GABA. A, SNB-1–CFP expression in GABAergic neurons of the ventral cord in an adult unc-25 mutant (arrows, motor neuron soma; arrowheads, synaptic varicosities). unc-25 encodes GAD, the biosynthetic enzyme of GABA, and in the mutant unc-25(e156), no GABA is detected (McIntire et al., 1993a). B, Localization of UNC-49–YFP in the ventral cord of the same animal. Presynaptic vesicle aggregates and GABA receptor clusters are colocalized in a pattern indistinguishable from what is observed in wild-type animals (arrowheads). Scale bar, 20 μm. C, UNC-49–YFP cluster size in the dorsal cord of wild-type (white) and unc-25(e156)(black) animals. Wild type, 0.56 ± 0.05 μm2 (average ± SEM; n = 3 worms; 95 clusters); unc-25, 0.59 ± 0.06 μm2 (n = 3 worms; 74 clusters). D, Fluorescence intensity of UNC-49–YFP clusters in wild type (white) andunc-25(e156) (black). Average ± SEM are, respectively, 80.96 ± 6.16 (n = 4 worms; 152 clusters) and 79.56 ± 5.71 (n = 8; 362) in the ventral nerve cord (VNC) and 67.85 ± 4.40 (n = 4; 100) and 66.17 ± 6.89 (n = 6; 182) in the dorsal nerve cord (DNC). E, Synapse densities in wild type (white) andunc-25(e156) (black). Average spacing ± SEM between clusters are, respectively, 3.19 ± 0.18 μm (n = 18 worms) and 3.31 ± 0.15 μm (n = 16) in ventral nerve cord (VNC) and 3.72 ± 0.26 μm (n = 15) and 3.52 ± 0.12 μm (n = 18) in dorsal nerve cord (DNC). F, Time course analysis of GABA receptor cluster formation in the dorsal cord of N2 (white) and unc-25(e156)(black) L2 larvae. As early as 23–24 hr after egg laying, synaptic varicosities are detected in 100% of L2 larvae, but the detection of GABA receptor clusters is delayed. UNC-49–YFP clusters are detected with a similar time course in wild-type (white) and unc-25(e156)(black) animals.
