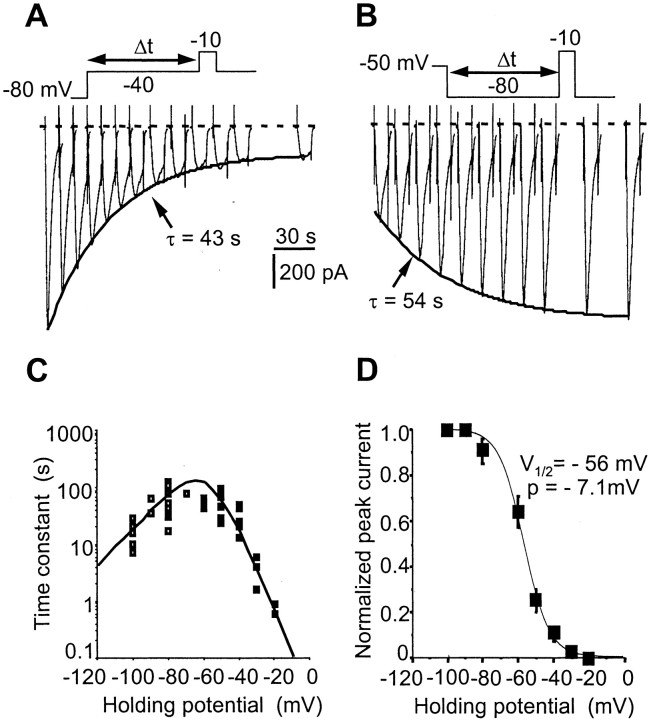
Fig. 7.
TTX-R INa ultraslow inactivation. A, Slow exponential decrease of TTX-RINa when the holding potential was stepped from –80 to –40 mV. The time scale refers to duration Δt at –40 mV. Test pulse duration, 50 msec.B, Same experiment as in A but with the holding potential stepped back from –50 to –80 mV. The TTX-RINa recovered its control amplitude exponentially with the indicated time constant. Test pulse duration, 50 msec. C, Voltage dependence of the on (filled squares) and off (open squares) processes of the ultraslow inactivation. Experiments were performed using a CsCl-based (140 mm) intracellular solution and 300 nm extracellular TTX. D, Steady-state ultraslow inactivation curve. Each point is the mean ± SEM for 12 AH neurons in which the holding potential was applied for 4 min. Data points were fitted to a Boltzmann function giving an ultraslow V1/2 of –56 mV and a p of –7.1 mV.