Fig. 3.
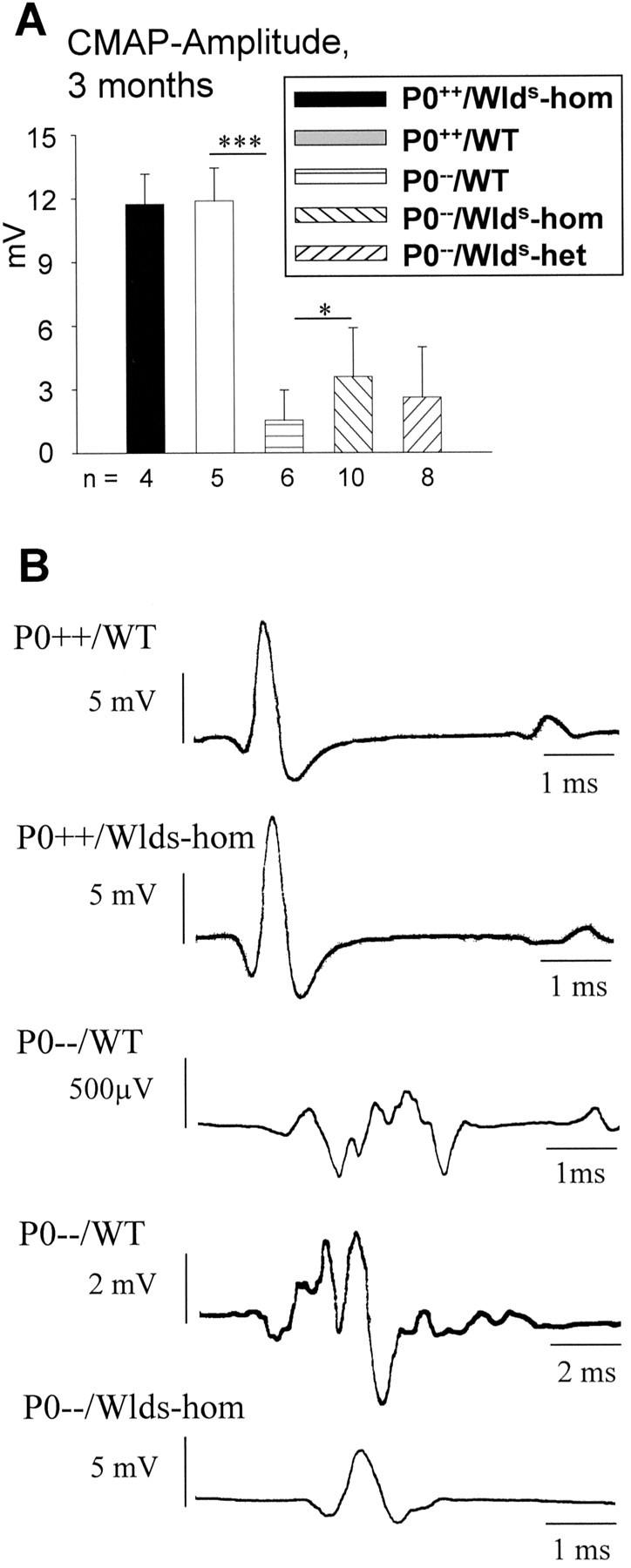
A, Schematic representation of amplitudes of compound action potentials from small foot muscles of 3-month-old P0+/+ and P0−/−mice with and without the Wldsmutation on distal stimulation of sciatic nerves. Note that theWlds mutation has no influence on amplitudes in P0+/+ genotypes. Amplitudes are markedly reduced in the absence of P0 (P0−/−), but reduction is less pronounced in the myelin mutants carrying the homozygousWlds mutation. Amplitudes from P0−/− mice heterozygous for theWlds mutation show a slight trend toward higher values compared with P0−/− single mutants. ***p < 0.0001 and *p< 0.05. n, Number of individuals of the respective genotype investigated. B, Original recordings of compound action potentials from small foot muscles of P0+/+ and P0−/− mice with and without the Wlds mutation on distal stimulation of sciatic nerves. Note the compact shape of muscle response in P0+/+ mice independent of theWlds mutation. P0−/− mice without theWlds mutation show predominantly dispersed responses, as shown here for two examples with relatively low and high amplitudes. Responses from P0−/−/C57BL/Wldsmice are usually more compact, as presented here for a typical case (lower recording). Note the different scales of time and amplitudes.CMAP, Compound muscle action potential;WT, wild type; hom, homozygous;het, heterozygous.
