Fig. 2.
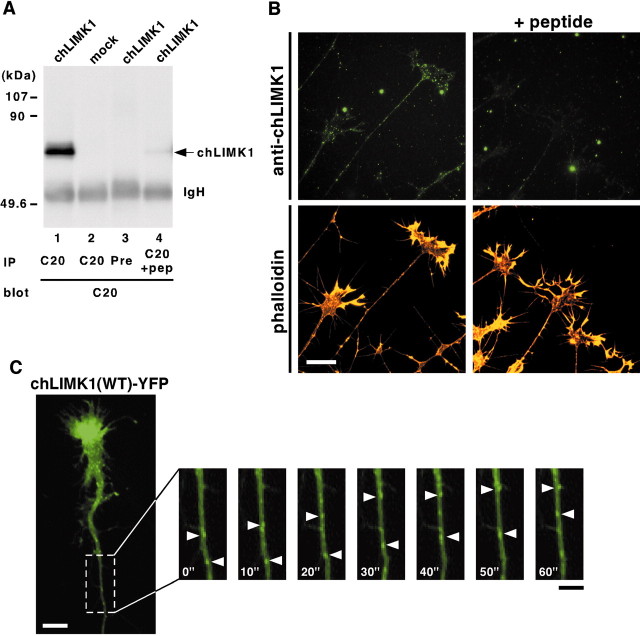
Subcellular localization of chLIMK1 in chick DRG neurons. A, Specificity of anti-chLIMK1 antibody. COS-7 cells were transfected with chLIMK1 cDNA expression plasmid (lanes 1, 3, 4) or mock-transfected with pMYC-C1 vector alone (lane 2). Lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with C20 anti-chLIMK1 antibody (C20,lanes 1, 2, 4) or preimmune serum (Pre, lane 3), run on SDS-PAGE, and then immunoblotted with C20 anti-chLIMK1 antibody. In lane 4, anti-chLIMK1 antibody was pretreated with excess amounts of antigenic peptide (pep). The positions of molecular weight marker proteins are indicated on the left.IgH, Ig heavy chain. B, Subcellular localization of chLIMK1 in chick DRG neurons. Chick E7 DRG neurons were costained with rhodamine-conjugated phalloidin (bottom) and C20 anti-chLIMK1 antibody (top) in the absence (left) or presence (right) of excess amounts of antigenic peptide. Dot-like staining of endogenous chLIMK1 was specifically detected in growth cones and axonal shafts at thetop left. Scale bar, 20 μm. C, Axonal transport of LIMK1(WT)-YFP. Chick E7 DRG neurons were infected with HSV coding for YFP-fused chLIMK1(WT) and recorded 12 hr later by video fluorescence microscopy. Each frame shows the fluorescence image of YFP at 10 sec intervals. Arrowheads indicate LIMK1(WT)-YFP-containing vesicles moving anterogradely. Also see the supplemental movie (available at www.jneurosci.org), in which retrograde movements can be seen. Scale bars: white, 10 μm; black, 5 μm.