Fig. 3.
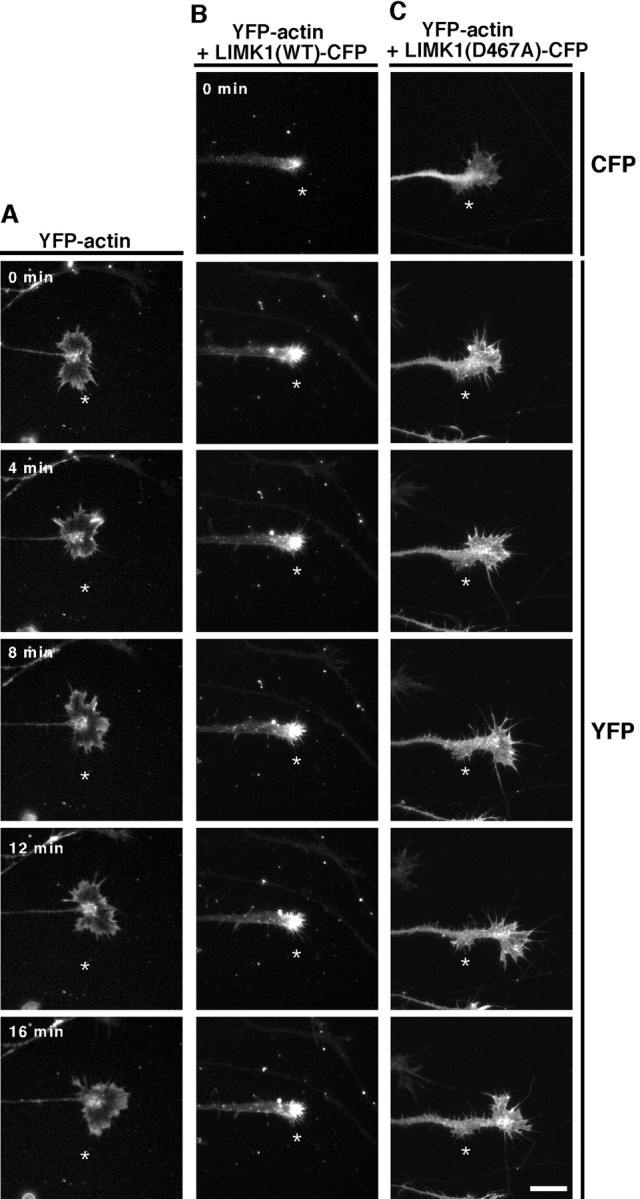
Time-lapse fluorescence images of growth cones expressing YFP-actin alone (A), YFP-actin plus CFP-tagged wild-type chLIMK1 [LIMK1(WT)-CFP] (B), or YFP-actin plus CFP-tagged D467A mutant of chLIMK1 [LIMK1(D467A)-CFP] (C). Chick E7 DRG neurons were infected with HSV encoding YFP-actin (A) or coinfected with HSV encoding YFP-actin plus HSV encoding LIMK1(WT)-CFP (B) or LIMK1(D467A)-CFP (C) and recorded 12 hr later by time-lapse video fluorescence microscopy. Cells expressing LIMK1(WT)-CFP or LIMK1(D467A)-CFP are assigned by CFP fluorescence, as shown in B (top) and C(top). Other frames show the fluorescence images of YFP-actin at 4 min intervals, as indicated in A. Theasterisk in each frame indicates the fixed point. Compared with the control growth cone in A, the growth cone expressing LIMK1(WT) was small and sticky and the growth cone motility and neurite extension were markedly suppressed. The motility of the growth cone expressing LIMK1(D467A) was slightly repressed. Scale bar, 20 μm. Also see the supplemental movies (available atwww.jneurosci.org). Quantitative data of growth cone motility and the rate of neurite extension of DRG neurons expressing YFP, LIMK1(WT)-YFP, or LIMK1(D467A)-YFP are summarized in Figure 5.
