Fig. 1.
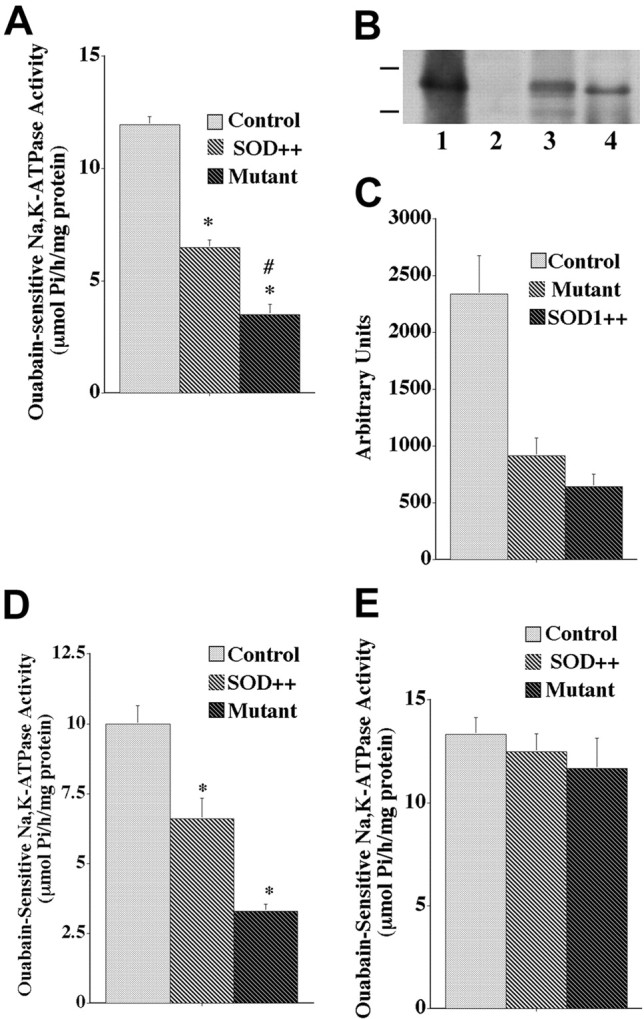
Ouabain-sensitive Na,K-ATPase activity in spinal cord and cerebellum of nontransgenic controls (Control), transgenic normal human SOD1 overexpressors (SOD++), and transgenic SOD1 mice (Mutant), and expression of normal and mutant human SOD1. For A and D, activity is expressed as μmol Pi/hr per milligram of protein.A, Spinal cord tissue slices from 4-month-old animals were homogenized, and ouabain-sensitive Na,K-dependent hydrolysis of ATP was determined. Values for activity represent the means ± SEM for an average of three samples in five experiments. *Significantly different from control at p < 0.05 (by ANOVA, Fisher's PLSD, and Scheffé's F test).#Significantly different from transgenic normal human SOD1 overexpressors at p < 0.05 (by ANOVA and Fisher's PLSD). B, Immunoblot detection of human SOD1 in nontransgenic controls (lane 2), transgenic mutant SOD1 mice (lane 3), normal human SOD1 overexpressors (lane 4), and purified human SOD1 as a positive gel control (lane 1). C, Densitometric analysis of human SOD1 expression levels in transgenic mutant SOD1 mice (Mutant), transgenic normal human SOD1 overexpressors (SOD++), and purified human SOD1 as a positive gel control. Values are expressed as arbitrary units and represent the means ± SEM for an average of three experiments.D, Na,K-ATPase activity was measured from cerebellar tissue slices from 4-month-old animals. Values represent the means ± SEM for an average of three samples in six experiments. *Significantly different from control at p < 0.05 (by ANOVA, Fisher's PLSD, and Scheffé's F test).E, Na,K-ATPase activity was measured in spinal cord tissue slice preparations from 2-month-old animals. Values for ouabain-sensitive Na,K-ATPase activity represent the means ± SEM for an average of three samples in three experiments.
