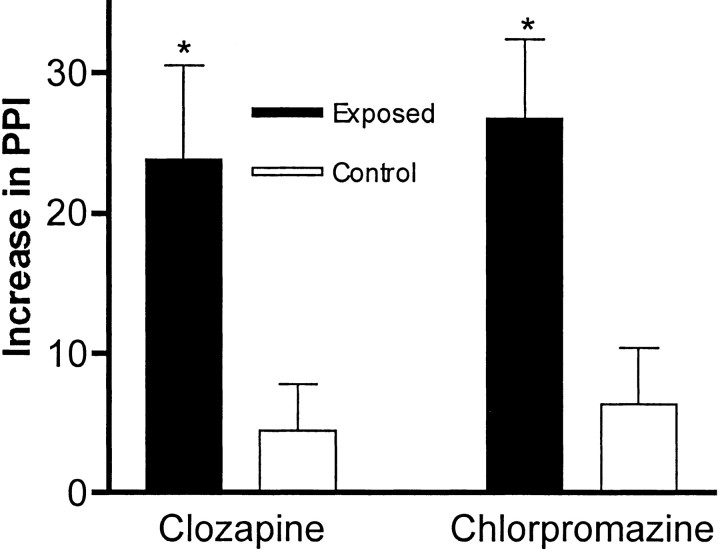
Fig. 6.
The effect of antipsychotic drugs on PPI. The typical antipsychotic drug chlorpromazine and the atypical antipsychotic drug clozapine were acutely administered to BALB/c mice, and PPI responses (with an 80 dB prepulse) were assayed. As expected from previous studies with rats, the sham-infected mice (Control) (n = 10; 5 females) displayed a modest increase in PPI when tested after drug injection. In contrast, the mice born to virus-infected mothers (Exposed) (n = 21; 12 females) displayed an extremely large increase in PPI after drug administration. The difference in the drug-induced increases between the control group and the experimental groups is significant (*p < 0.03). Note that the data are expressed as the percentage of PPI increase.