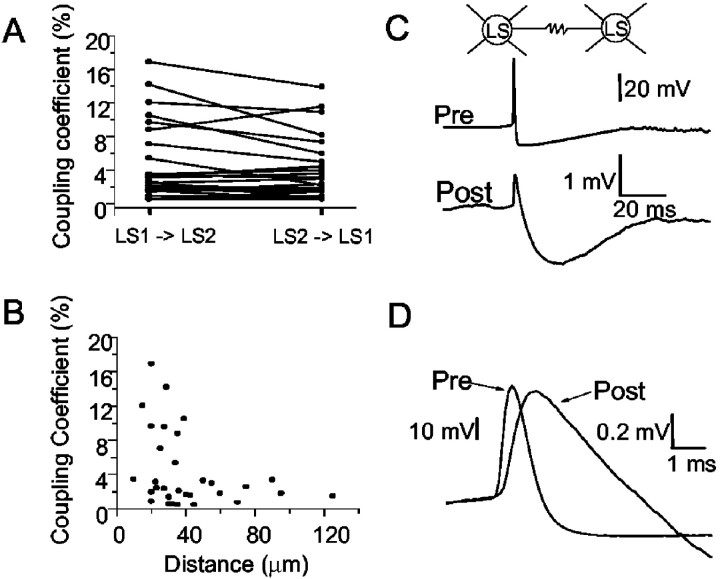
Fig. 8.
Properties of electrical coupling among layer 1 LS cells. A, Electrical coupling was bidirectional. Comparison of step coupling coefficient when current was injected in LS1 versus LS2. B, Step coupling coefficient as a function of the distance between the somata of the two electrically coupled LS cells (n = 31 pairs).C, Example of spike transmission in a pair of LS neurons that were connected only via electrical synapses (see Materials and Methods). A prolonged depolarization of the presynaptic cell produced spontaneous action potentials that were transmitted to a postsynaptic neuron as a brief depolarization, followed by a slow hyperpolarization. The holding potential of postsynaptic cell was −75 mV.Traces were aligned to the peak of the presynaptic spike and represent the average of 102 trials. The step coupling coefficient was 16.9%, and the spike coupling coefficient was 1.4%.D, Superimposition of the presynaptic spike and the corresponding response in the coupled postsynaptic neuron. The latency between the peak of presynaptic spike (Pre) and the peak of the spikelet or postsynaptic response (Post) was 0.7 msec. Data from the same pair as in C.