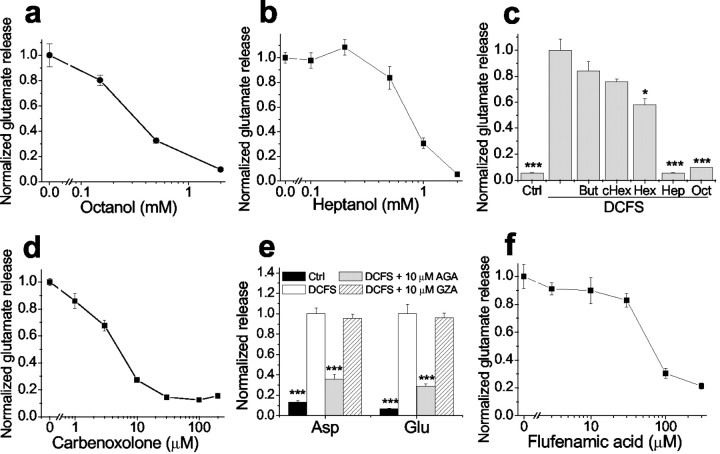
Fig. 3.
DCFS-induced glutamate release was blocked in a concentration-dependent manner by gap junction blockers but not by control compounds. a, Octanol. b, Heptanol. c, Shorter-chain alcohols (2 mm) had no effect or had less effect in reducing glutamate release compared with heptanol and octanol. But, Butanol; cHex, cyclohexanol; Hex, hexanol. d, Carbenoxolone. e, AGA but not GZA reduced glutamate release in DCFS. f, Flufenamic acid. n = 6–8 in all experiments; *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001; Control (ctrl) or blockers versus DCFS (by one-way ANOVA).