Fig. 2.
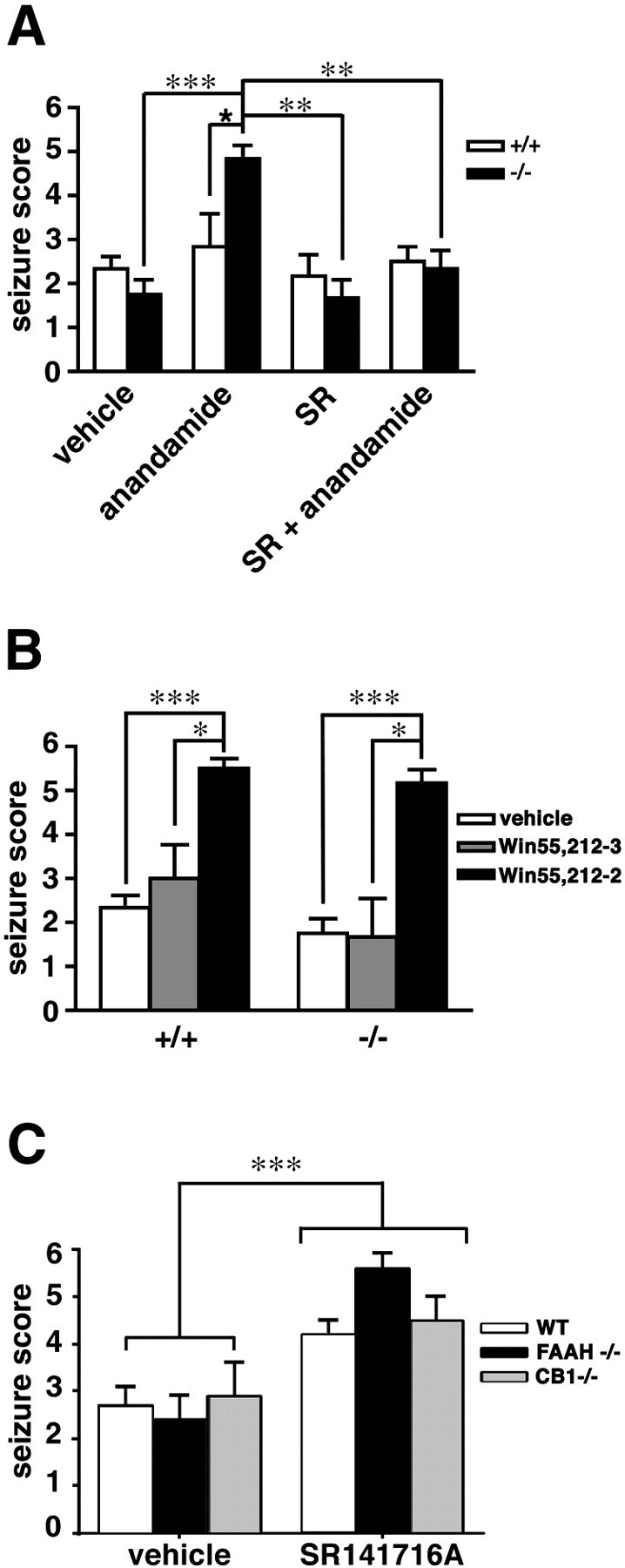
The effects of CB1 receptor agonists and antagonists on chemically induced seizures in FAAH (+/+) and (−/−) mice. A, FAAH (+/+) and (−/−) mice were treated with the CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716A (1 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle 10 min before administration of anandamide (25 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle. Seizures were induced with (bicuculline, 4 mg/kg, i.p.) 60 min after anandamide injection. SR141716A blocked the effects of anandamide on seizures in FAAH (−/−) mice but did not affect seizure responses in vehicle-treated animals of either genotype (SR group). n = 6–12 mice per group. ★p < 0.05 for FAAH (+/+) versus FAAH (−/−) mice receiving the same treatment. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 for FAAH (−/−) mice under different treatment conditions (Mann–Whitney U test).B, Treatment with the CB1 agonist (R)-(+)-WIN 55,212–2, but not its inactive enantiomer (S)-(−)-WIN 55,212–3 (15 mg/kg, i.p.), 1 hr before administration of bicuculline (4 mg/kg) significantly enhanced the severity of seizures in both FAAH (+/+) and (−/−) mice. n = 6–12 mice per group. *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 for WIN 55,212–2-treated versus WIN 55,212–3-treated and vehicle-treated mice of the same genotype, respectively (Mann–WhitneyU test). C, SR141716A augmented kainate-induced seizures in wild-type (WT), FAAH (−/−), and CB1 (−/−) mice. Subjects from each genotype were treated with either vehicle or SR141716A (1 mg/kg, i.p.) 70 min before kainic acid (15 mg/kg, i.p.). Data are depicted as means ± SEM (n = 8–14 FAAH (−/−) and CB1 (−/−) mice; 20–22 wild-type mice). ***p < 0.001 for SR141716A-treated versus vehicle-treated animals (ANOVA).
