Fig. 3.
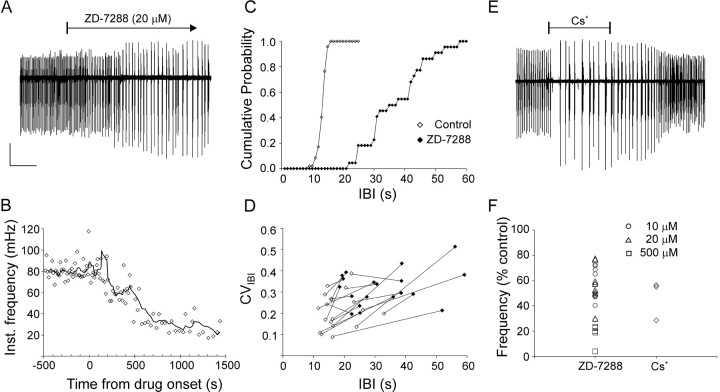
Blocking Ih strongly reduced nIB frequency and regularity. A, BlockingIh with the specific blocker ZD-7288 caused a more than threefold reduction in nIB frequency, coupled to a pronounced increase in nIB amplitudes. B, The time course of decrease in nIB frequency for the experiment shown inA, plotted at the same time scale. Data points represent instantaneous frequency (1/previous IBI); solid line is a running average, calculated using a sliding window of five data points. Time 0 designates drug arrival in the recording chamber. C, The rightward shift and decreased slope of the CIH for the experiment ofA illustrates the drug-induced increase in the IBI and the CVIBI, respectively. CIHs were calculated using 1 sec bins. D, CVIBI plotted against mean IBI, with data points from the same slice before (open symbols) and after (filled symbols) adding ZD-7288 connected by lines. Note that, in the great majority of cases, the ZD-7288-induced increase in the mean IBI was coupled to a pronounced increase in the CVIBI.E, A reduction in nIB frequency of a similar magnitude to that induced by ZD-7288 was caused by the less specific (but reversible) Ih blocker Cs+ (2 mm). F, Summary of the percent reduction in nIB frequency attributable to ZD-7288 (see legend for concentrations) and Cs+ (2 mm) in all experiments. A andE are from different P3 animals. Calibration:A, 100 μV, 300 sec; E, 150 μV, 250 sec.