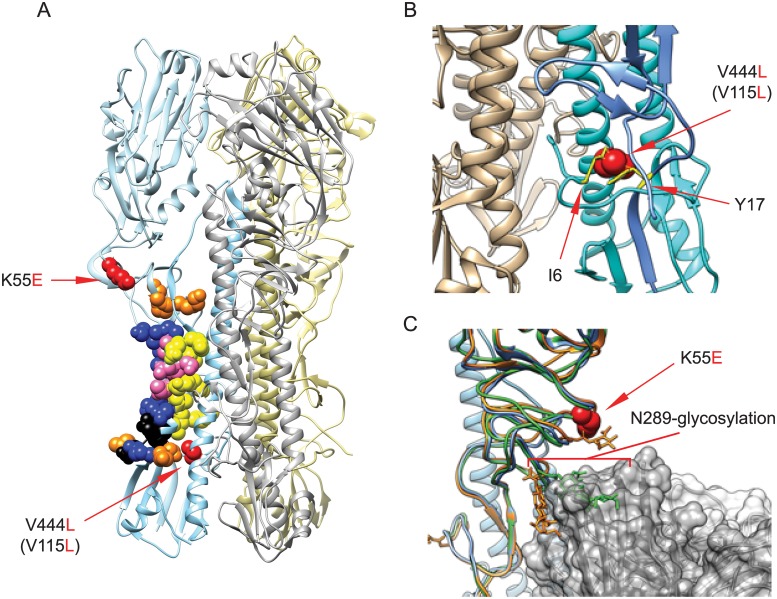
Fig 5. Stem antibody epitopes and MAb 4C2 resistance mutations.
(A) The localization of stem antibody epitopes and MAb 4C2 escape mutations in A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 HA trimer is shown. PDB: 1RU7. Yellow: C179 epitopes; Blue: CR6261 epitopes; Orange: FI6 epitopes; Pink: C179 and CR6261 overlap epitopes; Black: CR6261 and FI6 overlap epitopes; Red: MAb 4C2 escape mutations. (B) The changes of mutation V444L (V115L, HA2 numbering) in stem region. V444L (V115L) (red) is in HA2 helix B. The V to L substitution results in van der Waals clashes with residues I6 (HA2) and Y17 (HA1), colored in yellow. (C) The changes of mutation K55E in stem region. K55E (red) is located within a loop region containing HA1 residues 42–58 and 263–314. This region also includes N-linked glycosylation site N289, which has the potential to interfere with stem Ab binding. Shown is MAb FI6 (grey) and aligned HA1 structures from H1 –blue (1RU7), H1+FI6 –orange (3ZTN), and H2 –green (4HLZ). Alignment of HA1 causes N289-glycosylation to clash with the bound antibody in some conformations (green), but not others (orange).