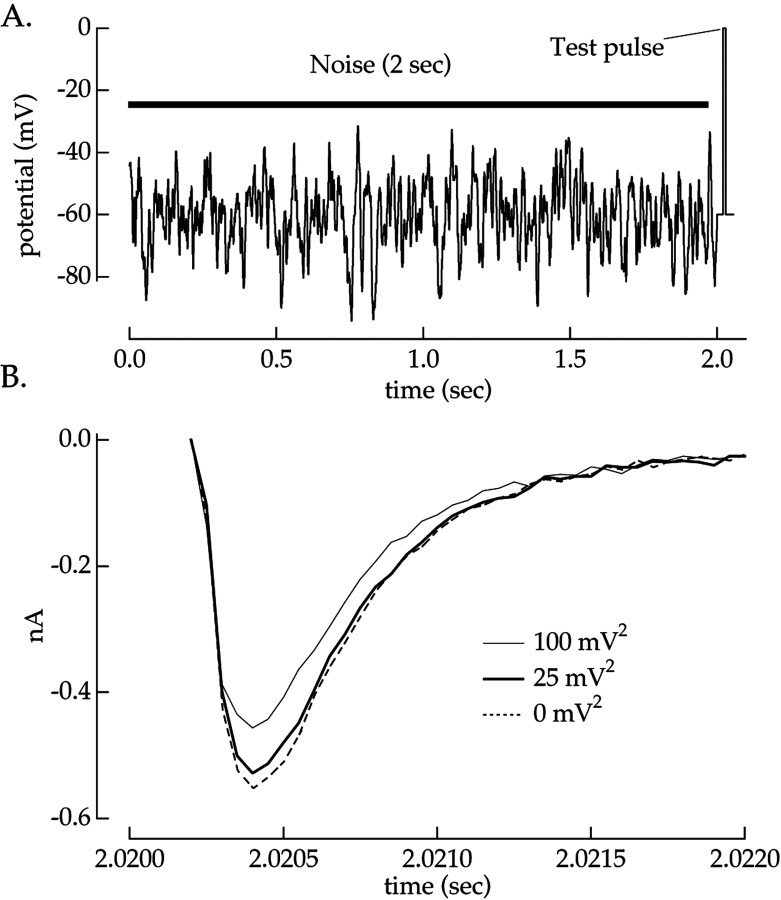
Fig. 3.
Na+ current is sensitive to preceding voltage fluctuations. A, Voltage-clamp stimulus. The Na+ current was measured in response to a brief test pulse to 0 mV after 2 sec of Gaussian voltage fluctuations (bandwidth, 0–50 Hz). A 20 msec recovery period at a holding voltage of −60 mV was imposed between the noise and test pulse. B, Average Na+ currents after noise with variances of 0, 25, and 100 mV2 are shown. Responses from four pulses after uncorrelated noise stimuli were averaged together to prevent the specific immediate history of the noise from affecting the Na+ current.