Fig. 1.
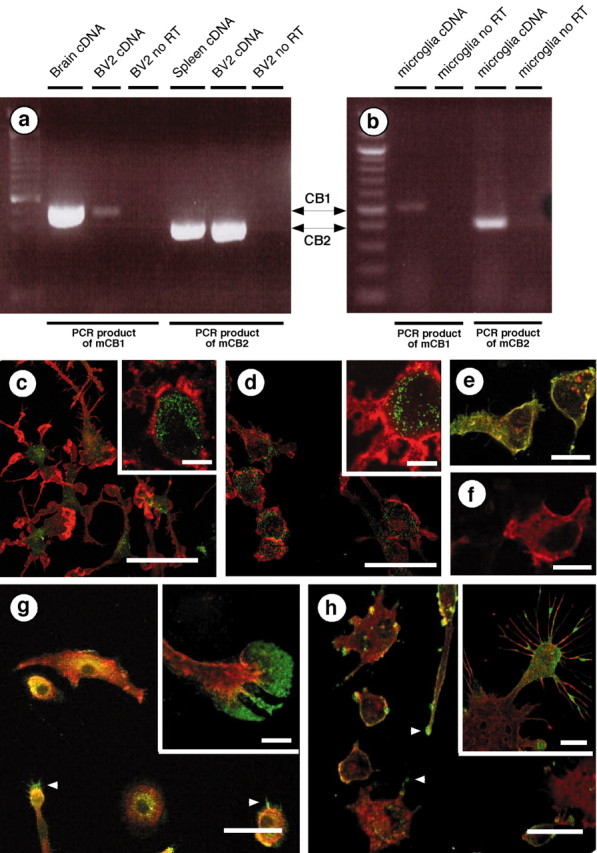
Microglial cells express cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. a, b, RT-PCR was performed with primers that recognize either mouse CB1 (mCB1) or mouse CB2 (mCB2) mRNA. We used reverse-transcribed total RNA from mouse brain and spleen (i.e., positive controls), BV-2 cells, and mouse microglial cells. RT-PCR products were of the appropriate size (502 bp for CB1 and 401 bp for CB2) and sequence. c–h, Immunofluorescent confocal microscopy. Mouse microglial cells (c) and BV-2 cells (d) were stained with an antibody directed against the CB1 C terminus (green) and phalloidin to label actin (red). Scale bars, 50 μm. Insets, Higher magnifications of the CB1 receptors (green) located in the intracellular compartment (MAC1, a plasma membrane macrophage marker, is in red). Scale bars, 10 μm. e, HEK293 cells transiently transfected with rat CB2 receptors tagged with HA11 (red) and stained with antibodies directed against CB2 C terminus (green). Colocalization isyellow. f, Similar immunostaining as ine, but performed in the presence of the immunizing antigen (i.e., the last 42 aa of the mouse CB2 receptor C terminus). Scale bars, 35 μm. Mouse microglial cells (g) and BV-2 cells (h) stained with antibodies directed against the CB2 receptor C terminus (green) and phalloidin (red).Arrowheads indicate CB2 receptors located at the lamellipodia tip. Scale bars, 50 μm. Insets, Higher magnification showing CB2 receptors at the leading edges of lamellipodia (g) and on microspikes (h). Scale bars, 10 μm.
