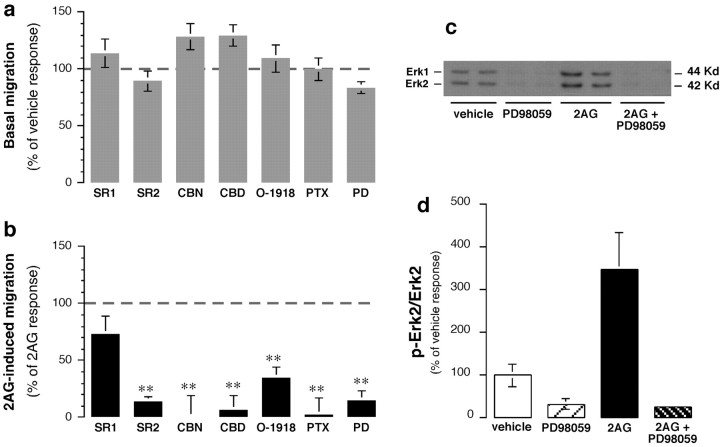
Fig. 4.
2-AG increases microglial cell migration by acting through CB2- and CBD-sensitive receptors and stimulating ERK1/2 activity. a, Effects of various agents on basal migration. Values in a and b are means ± SEM of 9–36 independent quantifications of migration (i.e., 3–12 separate experiments performed in triplicate). Agents that were added to the lower chamber are as follows: 30 nmSR141716A (SR1), 30 nm SR144528 (SR2), 300 nm CBN, 300 nm CBD, 1 μm O-1918, or 10 μm PD98059 (PD). To test for the involvement of Gi/o-proteins, BV-2 cells were pretreated with 1 μg/ml pertussis toxin (PTX) for 18 hr.b, Effects of various agents on 2-AG (2AG)-induced migration. Results are expressed as a percentage of the control 2-AG-induced migration determined in each experiment (i.e., migration induced by 1 μm 2-AG added alone to the lower chamber minus corresponding basal migration obtained with the same agent; dashed line; see a). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; significantly different from the control 2-AG response (Student'st test). c, Representative Western blot with phospho-ERK1/2 antibodies. d, Quantification of three separate experiments performed in duplicate (n = 6). **p < 0.01; significantly different from basal (ANOVA followed by Dunnett'spost hoc test).