Fig. 1.
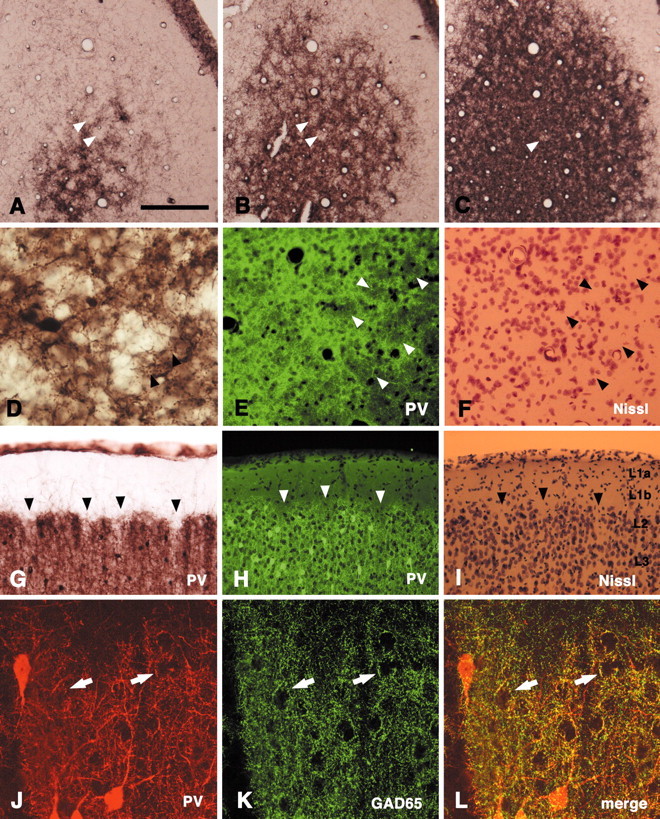
PV immunoreactivity shows a honeycomb pattern in superficial layers in the rat V1. A–C, Serial tangential sections stained by immunoperoxidase method for PV. PV-ir walls surround open hollows (arrowheads).D, Higher magnification. Arrowheads point to PV-ir terminal-like puncta. E, F, Tangential section. Double staining for PV (immunofluorescence,E) and Nissl substance (F) shows that the hollows tend to contain fewer cells than do the walls.Arrowheads point to corresponding spaces.G, Coronal section stained by immunoperoxidase method for PV. The hollows are less conspicuous but can be detected as a series of notches (arrowheads). H, I,Coronal section. Double staining for PV (H) and Nissl substance (I) confirms that the honeycomb is located at the level of layer 2. Arrowheads point to corresponding hollows. J–L, Coronal section. Double-immunofluorescent staining for PV and GAD65 demonstrates colocalization of these two markers, as expected if the small PV-ir particles were GABAergic terminals. Double-labeled structures frequently made basket-like terminations on immunonegative somata (arrows). Scale bar (shown in A):A–C, 200 μm; D, 80 μm; E–I, 100 μm;J–L, 25 μm.
