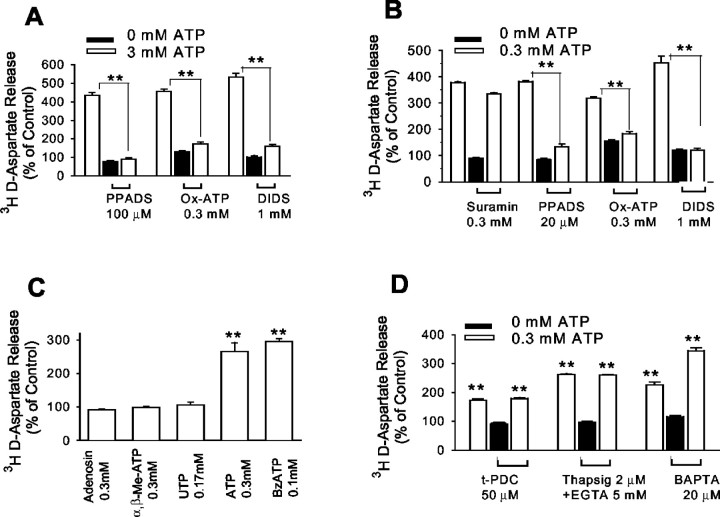
Fig. 7.
Pharmacology of ATP-inducedd-aspartate release indicates action at P2X7receptors. A, Standard BSS. B–D, Ca2+/Mg2+-free BSS.A, ATP-induced d-aspartate release is blocked by DIDS, by the P2 receptor antagonist PPADS, and by a 2 hr preincubation with the irreversible P2X7-selective inhibitor Ox-ATP. B, ATP was ∼10-fold more potent in Ca2+/Mg2+-free medium than in standard medium (compare with A). The P2X7receptor inhibitors also blocked ATP-induced d-aspartate release in Ca2+/Mg2+-free medium, whereas the P2X1 antagonist suramin was ineffective.C, d-Aspartate release was induced by BzATP and ATP but not by agonists of other purinergic receptor subtypes.Adenosin, Adenosine; α,β-Me-ATP, α,β-methylene ATP. D, ATP-induced release was not attenuated by preloading with PDC to block glutamate uptake reversal, by preloading the astrocytes with the calcium chelator BAPTA, or by depleting cell calcium with preincubation in Ca2+-free medium containing EGTA and thapsigargin (Thapsig). Preincubations with PDC, BAPTA-AM, and EGTA/thapsigargin were performed at 37°C for 40 min and followed by exchange with Ca2+/Mg2+-free BSS before thed-aspartate release assay. Values in eachpanel are means ± SE; n ≥ 6. **p < 0.01.