Fig. 4.
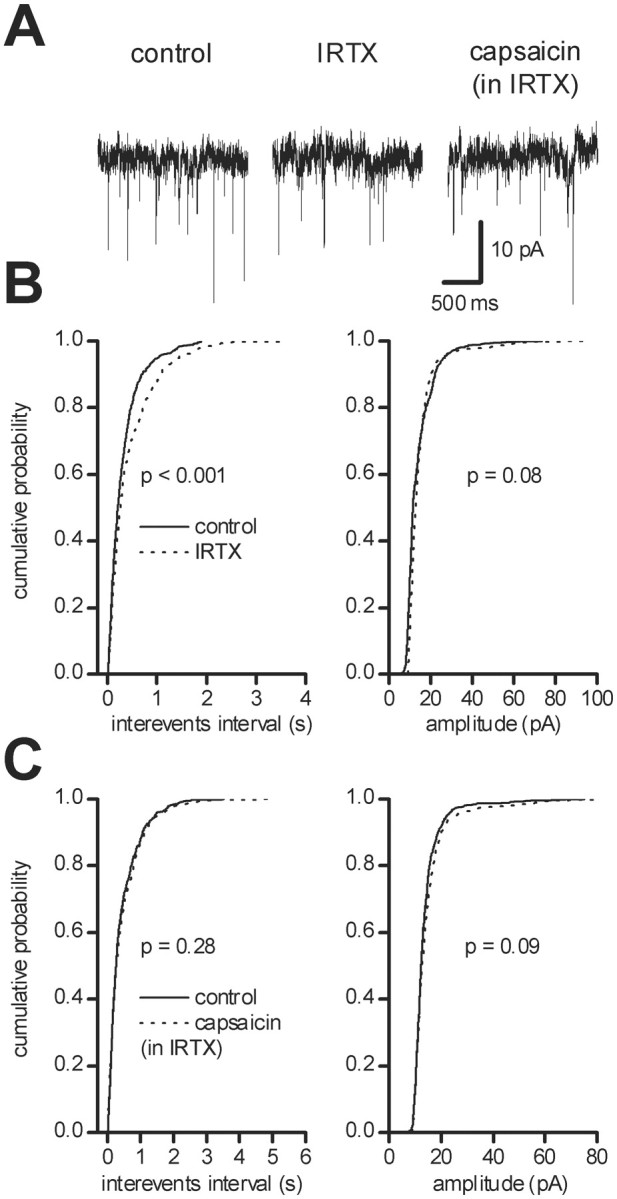
Tonic control of glutamatergic neurotransmission by VR1s. Recordings were performed in the presence of picrotoxin (100 μm). A, Trace records from a single dopaminergic neuron under control conditions (left) and in the presence of the VR1 antagonist IRTX (300 nm, middle). Under these conditions, sEPSC frequency was reduced. In the presence of IRTX, capsaicin (10 μm) was no longer able to produce a facilitation of glutamatergic neurotransmission (right).B, Cumulative probability distributions of interevent intervals (left) and of peak amplitude (right) from the neuron shown inA in controls (solid line) and in the presence of 300 nm IRTX (dotted line). C, Cumulative probability distributions of interevent intervals (left) and of peak amplitude (right) of the neuron shown in A in 300 nm IRTX (solid line) and in IRTX plus 10 μmcapsaicin (dotted line).
