Fig. 2.
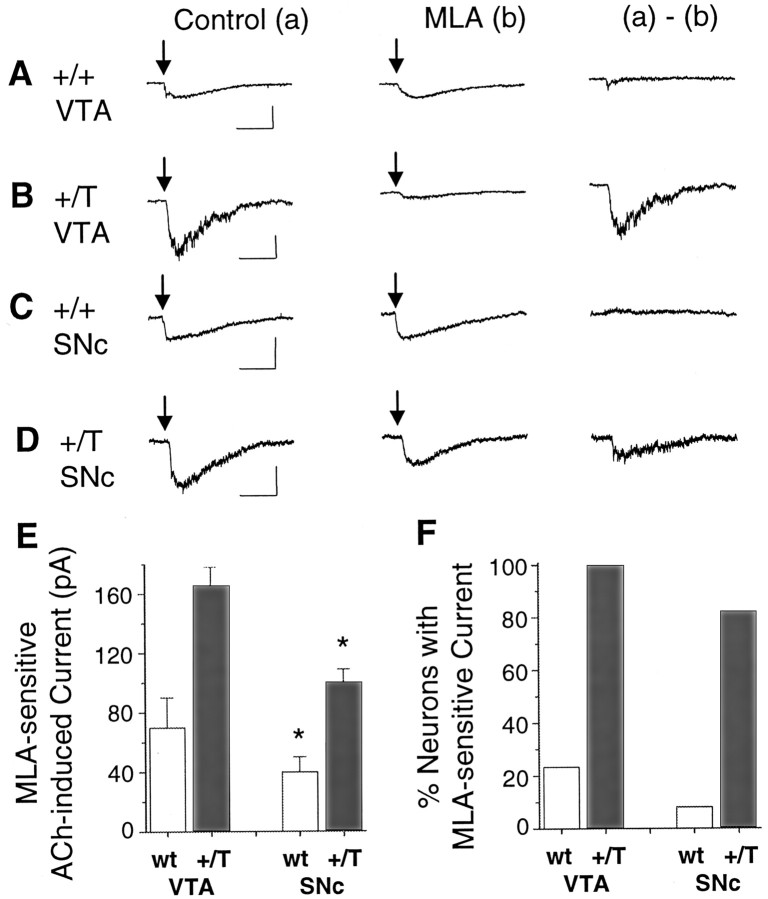
Mice expressing mutant α7L250T subunits display much larger MLA-sensitive currents. Pressure applications of 1 mm ACh (arrows) elicited currents from a wild-type VTA DA neuron (A), from a mutant +/T VTA DA neuron (B), from a wild-type SNc DA neuron (C), and from a mutant +/T SNc DA neuron (D). In each case, (a) denotes the control current and (b) denotes the current recorded in the presence of MLA. The (a) − (b)subtraction shows the net MLA-sensitive current. As expected, the α7L250T mutation produces larger and slower ACh-induced currents. The ACh puffs were 30–60 msec in duration for A,B, and D, but 200 msec inC. E, The bar graphs compare the magnitude of the MLA-sensitive currents in the VTA or SNc and from wild-type or +/T mice. F, The bar graphs compare the proportion of the sampled neurons with MLA-sensitive current in the VTA or SNc and from wild-type or +/T mice. Calibration: 200 pA (A, B), 50 pA (C, D), 0.5 sec. *p < 0.05 significantly different from corresponding VTA values by Student's t test.