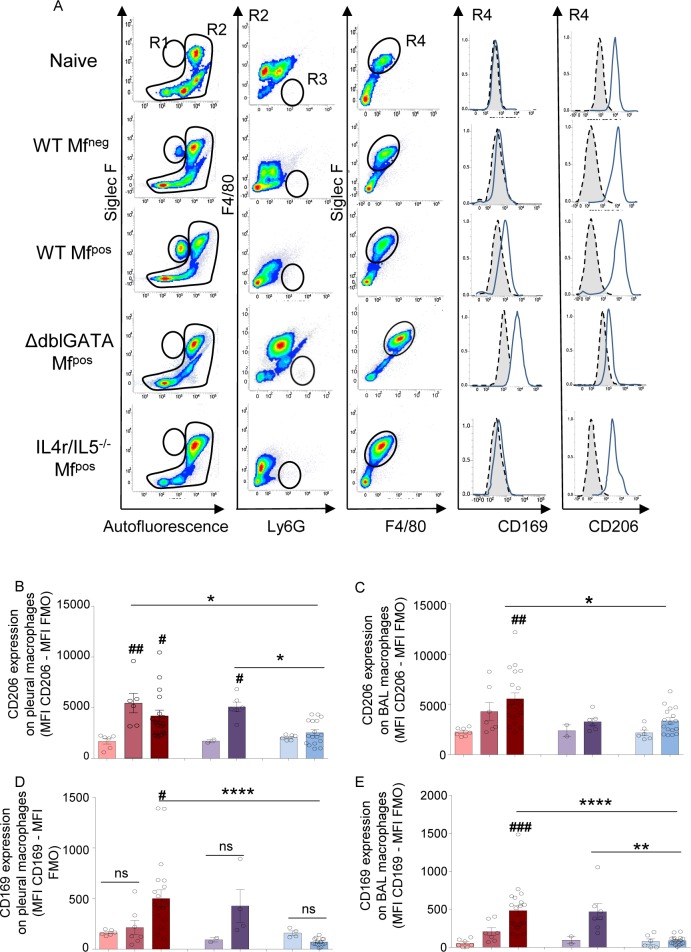
Fig 7. Activation of macrophages in infected mice is dependent on IL-4R and/or eosinophils.
Pleural and bronchoalveolar cells were isolated from L. sigmodontis infected WT, ΔdblGata1 and Il-4ra-/-/Il-5-/- BALB/c mice at 70 days p.i. Macrophage activation (CD206 and CD169 expression) were analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Representative plots and curves showing the gating strategy for bronchoalveolar cells stained with anti-SiglecF-PE, anti-F4/80-APC, anti-Ly6G-V450, anti-CD169-FITC and anti-CD206-PE-Cy7. Doublets and dead cells were excluded prior further analysis. R1 = SiglecF+ eosinophils. R2 = Non-eosinophil cells. R3 and R4 were defined from the R2 population: R3 = Ly6G+ neutrophils; R4 = F4/80+ macrophages; CD206 and CD169 expressions were measured on R4 population (F4/80+ macrophages). Gray area represents the FMO signal. (B) CD206 expression on pleural macrophages; (C) CD206 expression on bronchoalveolar macrophages; (D) CD169 expression on pleural macrophages; (E) CD169 expression on bronchoalveolar macrophages. Both CD206 and CD169 expressions were normalized by subtracting the FMO signal. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM of n = 6–7 WT naïve, n = 7 WT Mfneg, n = 19–20 WT Mfpos; n = 2 ΔdblGata1 naïve; n = 5–7 ΔdblGata1 Mfpos; n = 6 Il-4ra-/-/Il-5-/- naive; n = 17 Il-4ra-/-/Il-5-/- Mfpos. Differences between infected groups and respective naïve groups were analyzed by a One-way ANOVA (after checking the conditions of application of the test): #p<0.05, ##p<0.01, ###p<0.001. Differences between Mfpos groups *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001 groups were also analyzed by a One-way ANOVA.