Figure 1.
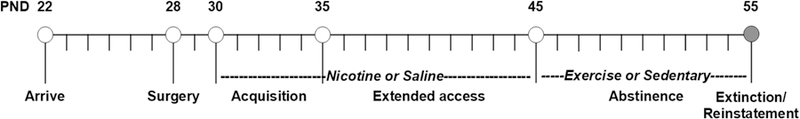
Summary of the experimental time-line as a function of postnatal day (PND). Rats arrived at PND 22, and following a 6-day habituation period, underwent jugular catheterization surgery on PND 28. A 5-day self-administration training period began following recovery on PND 30 wherein rats had fixed ratio 1 access to 20 nicotine or saline infusions/day. A 10-day extended access period began on PND 35 wherein rats had access to an unlimited number of infusions for 23-hours/day. During the 10-day abstinence period that followed, rats had 2-hour/day access to an unlocked (exercise) or locked (sedentary) running wheel (PND 45–54). After the last exercise/sedentary session, rats were returned to their self-administration boxes. Nicotine-seeking was assessed the next day on PND 55 using a within-session extinction/cue-induced reinstatement procedure.
