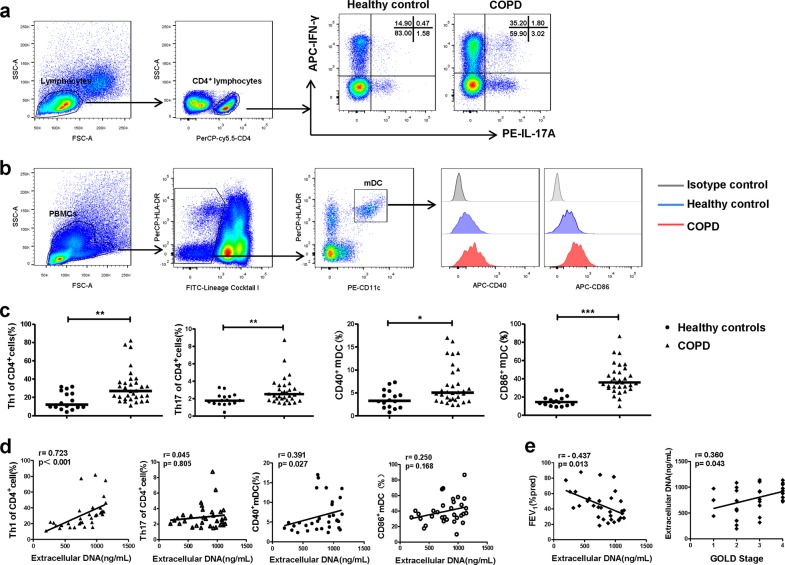
Fig. 4. Correlations between extracellular DNA in the sputum, and Th1/Th17 responses, and the activation of DCs in COPD.
a Peripheral bloods of mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of 16 healthy controls and 32 COPD patients were isolated by Lymphoprep centrifugation and detected by flow cytometry. Lymphocytes of PBMCs were identified based on forward-scattered light (FSC) and side-scattered light (SSC). Th1 cells were identified by CD4+IFN-γ+ cells and Th17 cells were identified by CD4+IL-17+ cells. Representative scatter plots of Th1 cells and Th17 cells of healthy controls and patients with COPD were shown. b PBMCs were identified based on FSC and SSC. The mDCs were identified by CD11c+HLA-DRhigh cells in FITC-Lindim/negative cells. Representative histograms of CD40 and CD86 of mDCs in healthy controls and COPD were shown. c The proportions of Th1 and Th17 cells in CD4+ cells and the proportions of CD40+ and CD86+ mDCs in PBMCs of 16 healthy controls and 32 patients with COPD. Data are expressed as medians. The comparisons were determined by Mann–Whitney test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. d The correlations between extracellular DNA in sputum of COPD patients and circulating Th1 and Th17 cells and CD40 and CD86 on mDCs in PBMCs were determined by Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient. e The correlations between extracellular DNA in sputum of COPD patients and the ratio of actual FEV1 to predicted FEV1 (FEV1% pred), and GOLD stage were determined by Spearman’ s rank correlation coefficient