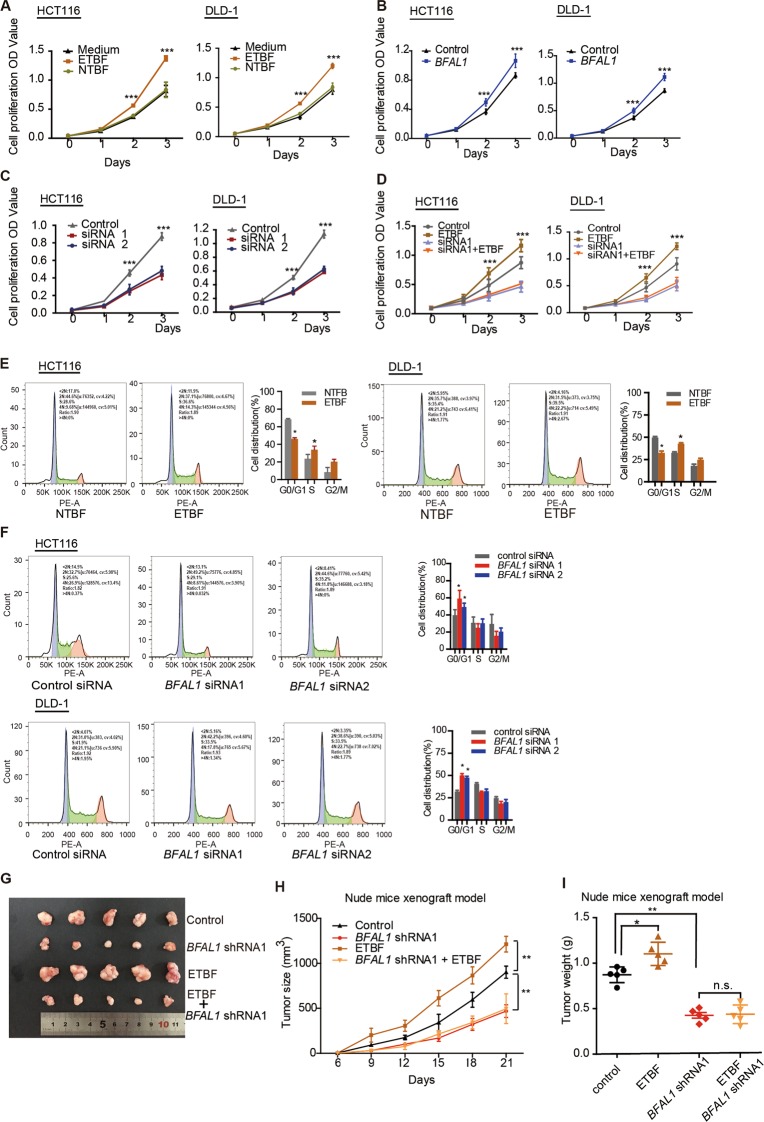
Fig. 2. ETBF exerts a biological function on CRC cell growth via BFAL1 in vitro and in vivo.
a CCK-8 assay of ETBF-treated HCT116 cells and DLD-1 cells compared with NTBF or single bacterial medium-treated cells (n = 6, ANOVA, ***P < 0.001). b CCK-8 assay of BFAL1 overexpression and control cells (n = 6, ANOVA, ***P < 0.001). c CCK-8 assay of BFAL1 knockdown in HCT116 cells and DLD-1 cells (n = 6, ANOVA, ***P < 0.001). d CCK-8 assays of ETBF-treated, BFAL1 knockdown HCT116 cells and DLD-1 cells (n = 6, ANOVA, ***P < 0.001). e Cell cycle analysis of ETBF-treated HCT116 cells and DLD-1 cells (mean ± SD of three independent experiments; ANOVA, *P < 0.05). f Cell cycle analysis of BFAL1 knockdown of HCT116 cells and DLD-1 cells (mean ± SD of three independent experiments; ANOVA, *P < 0.05). g Xenograft tumors in the nude mouse model under different treatments (n = 5). h Statistical analysis of tumor sizes (mean ± SD, n = 5, ANOVA, **P < 0.01). i Tumor weights of different mouse groups (mean ± SD, n = 5, ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01)