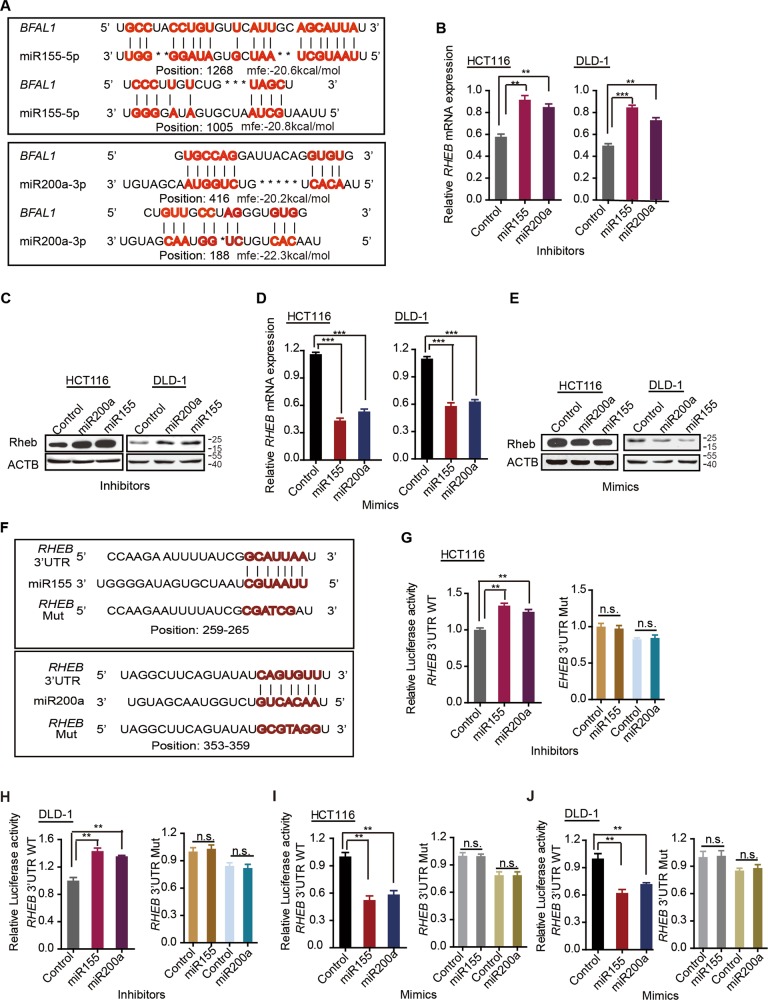
Fig. 4. miR-155-5p and miR-200a-3p target the RHEB 3ʹ UTR.
a The predicted binding sites of miR-155-5p and miR-200a-3p on the BFAL1 transcripts. b RHEB mRNA levels in HCT116 cells and DLD-1 cells treated with inhibitors of miR-155-5p or miR-200a-3p. c RHEB levels in HCT116 cells and DLD-1 cells transfected with inhibitors of miR-155-5p or miR-200a-3p. d RHEB mRNA levels in HCT116 cells and DLD-1 cells transfected with mimics of miR-155-5p or miR-200a-3p. e RHEB levels in HCT116 cells and DLD-1 cells transfected with mimics of miR-155-5p or miR-200a-3p. f The predicted miR-155-5p and miR-200a-3p binding sites on the RHEB 3′ UTR and the mutated sites. g, h Luciferase reporter assays were performed in HCT116 cells and DLD-1 cells transfected with inhibitors of miR-155-5p or miR-200a-3p. The luciferase reporters expressing wild-type or mutant human RHEB 3ʹ UTR were used (data represent mean ± SD of three independent experiments, ANOVA, **P < 0.01). i, j Luciferase reporter assays were performed in HCT116 cells and DLD-1 cells transfected with mimics of miR-155-5p or miR-200a-3p. The luciferase reporters expressing wild-type or mutant human RHEB 3ʹ UTR were used (data represent mean ± SD of three independent experiments, ANOVA, **P < 0.01)