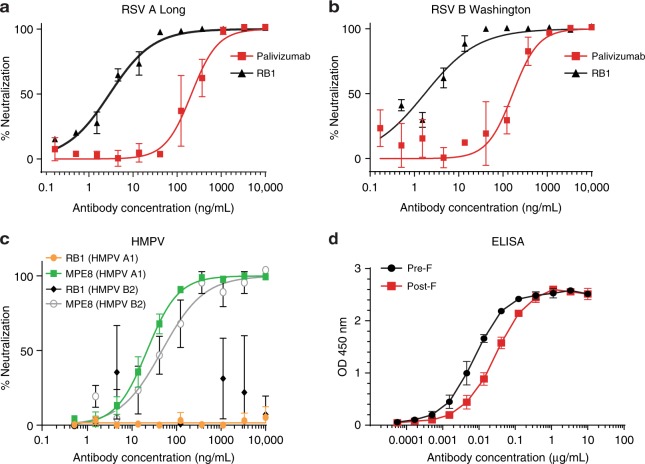
Fig. 1.
In vitro binding and neutralization. a The neutralization activity of RB1 against laboratory strains RSV A (Long) and b RSV B (Washington) with palivizumab as an assay control antibody. Assays were run in duplicate, showing error bars at mean with standard deviation (SD). An IC50 was calculated using a log versus response variable slope 4 parameter fit curve and represents the concentration of antibody required for a 50% reduction in the RSV infectivity in a microneutralization assay. c The neutralization activity of RB1 against laboratory strains HMPV A and B with MPE8 control antibody. Assays were run in triplicate, showing error bars at mean with standard deviation (SD). An IC50 was calculated using a log versus response variable slope 4 parameter fit curve and represents the concentration of antibody required for a 50% reduction in the HMPV infectivity in a microneutralization assay. d The enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) binding curves of RB1 binding to the pre-F and post-F protein conformations. The assay was run in duplicate showing error bars at mean with SD. An EC50 was calculated and represents the concentration of antibody required for a 50% reduction in binding. Source data provided as a source data file