Fig. 6.
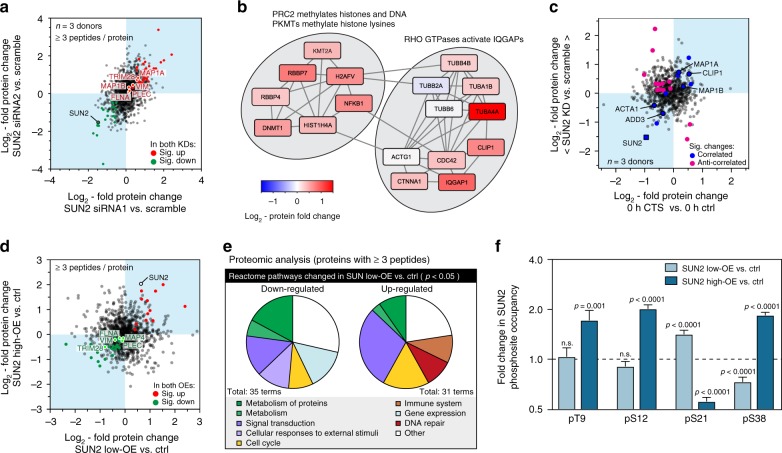
Knockdown (KD) and overexpression (OE) of SUN2 affect the cellular proteome. a MS characterization of SUN2 KD on protein levels in primary hMSCs. Plot shows correlation between log2-fold changes to the proteome following SUN2 KD with two siRNAs, siRNA1 and siRNA2, each measured relative to scrambled controls (n = 3 donors; see Supplementary Figs. 9a, b for histograms). Data points annotated as indicated in the legend where significant changes occurred (p < 0.05), otherwise they are shown in gray. b Pathways identified in the Reactome database35 as significantly affected by both SUN2 KDs, relative to scrambled controls, shown with fold changes to constitutive proteins. c Correlation between changes to protein levels following SUN2 KD (mean of both siRNA treatments, relative to scrambled controls) and immediately following CTS (1 h, 2.6–6.2% strain at 5 Hz relative to unstrained controls). Correlated and anti-correlated data annotated as indicated in the legend where significant changes occurred (p < 0.05; n = 3 donors), otherwise they are shown in gray. d MS characterization of SUN2 OE in an immortalized human MSC line. Plot shows correlation between log2-fold changes to the proteome following SUN2 OE with two separate expression levels, low (160% of control following 3 days of DOX treatment) and high (410% of control following 4 days of DOX treatment), measured relative to vehicle-only controls (n = 3 replicates; see Supplementary Figs. 9c, d for histograms). Data points annotated as indicated in the legend where significant changes occurred (p < 0.05), otherwise they are shown in gray. e Analysis of Reactome pathways significantly affected at the protein level following SUN2 low-OE (p < 0.05). Protein quantification in a–e based on ≥3 peptides-per-protein. f Quantification of SUN2 phosphosites following low and high OE, as characterized in d. pS21 and pS38 were significantly affected by low SUN2 OE (p < 0.0001); high OE significantly affected pT9 (p = 0.001), pS12, sS21, and pS38 (p < 0.0001). n = 3 technical replicates. Data displayed as mean and s.e.m. All p-values were calculated using empirical Bayes-modified t-tests with Benjamini–Hochberg correction. See Supplementary Data 10–13