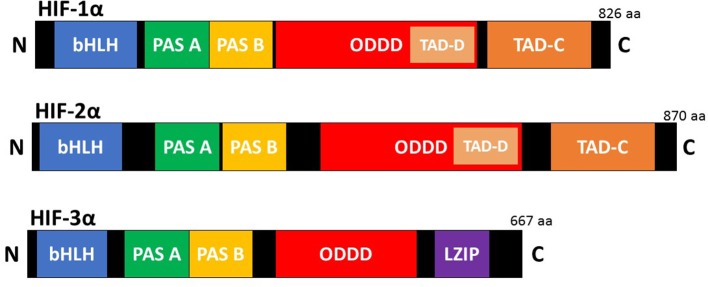
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the domain structure of the HIF-α members. HIF-α consists of a bHLH (basic helix loop helix) and PAS (Per-ARNT-Sim homology) domain in the NH2-terminal, which are necessary for heterodimerization and DNA binding to the hypoxia response elements (HRE). Two transactivation domain(s) (TAD), which stimulate transcription, are present in the COOH-terminal of HIF-1α, and HIF-2α. TAD-C interacts with coactivators such as CBP/p300 to activate gene transcription. HIF-3α has a leucine zipper (LZIP) domain but lacks the TAD-C domain present in HIF-1α and HIF-2α.HIF-α also contains an oxygen-dependent-degradation (ODD) domain, which contains the conserved proline(s) hydroxylated by PHD and FIH to promote proteasomal degradation.