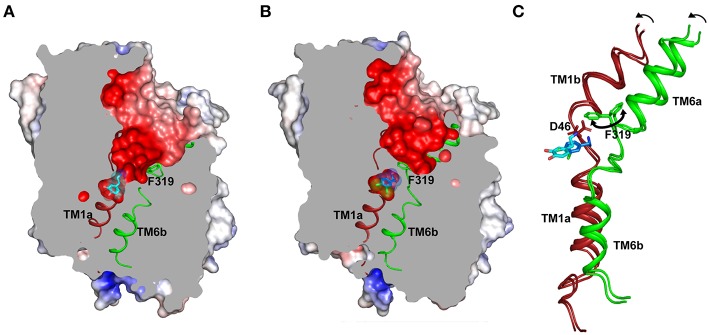
Figure 4.
(A) Structure displays the outward-open conformation of dopamine bound dDAT with the primary substrate binding site open to the extracellular vestibule and solvent access. The gating residue F319 (TM6, green) is displayed to indicate its role in control of the extracellular gates (PDB ID: 4XP1). (B) Inward movement of F319 occludes the binding pocket and separates the substrate analog (DCP) from extracellular vestibule (PDB ID: 4XPA). (C) Inward movement in the gating helices TM1b, 6a to form an occluded state. F319 swings in (100°) to occlude the binding site. The D46 undergoes a 120° torsional angle shift to interact with the primary amine of dopamine.