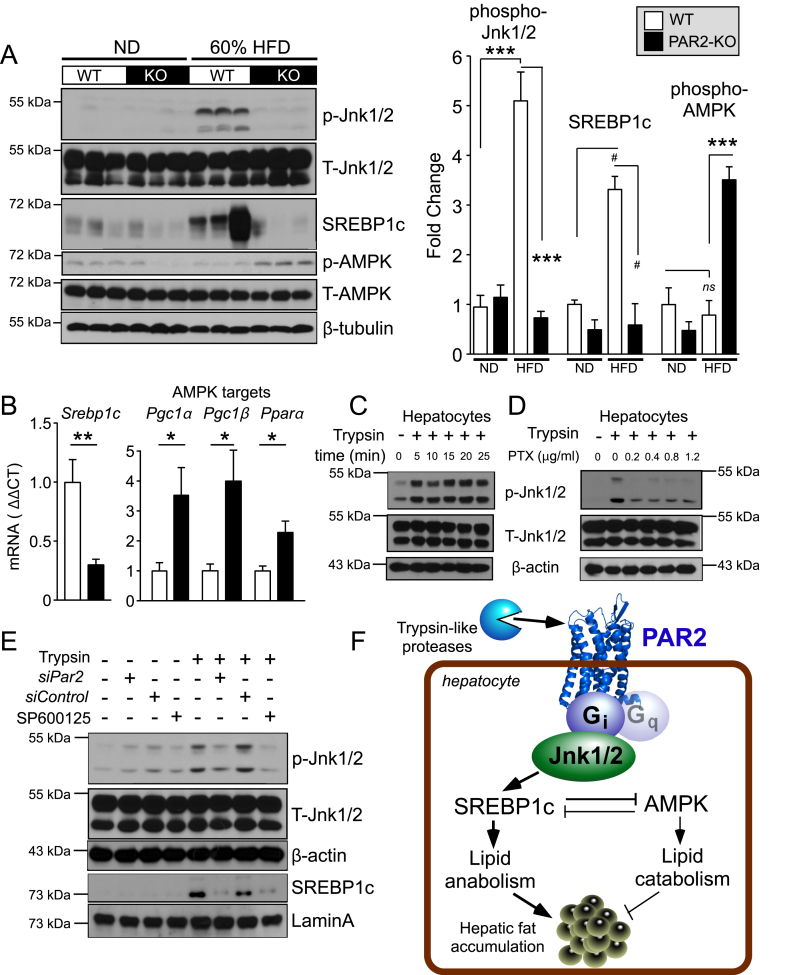
Figure 6.
PAR2-Gi activates JNK-SREBP-1c pathways that induce hepatic lipid accumulation in HFD-fed mice. (A) Western blots of liver lysates from WT and PAR2-KO mice fed either normal chow diet (ND) or high fat diet (HFD) for 16 weeks. Densitometric quantification of western blots on left for Phospho (P)-Jnk1/2 normalized to total (T)-Jnk1/2, active 65 kDa proteolytic fragment of SREBP-1c normalized to β-tubulin, and Phospho (P)-AMPK normalized to total-AMPK. (B) Quantitative PCR (ΔΔCT) of mRNA from mouse liver (n = 5) normalized to β-actin mRNA of Srebp1c and AMPK targets: Pgc1α (peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, gamma, coactivator 1 alpha), Pgc1β (peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, gamma, coactivator 1 beta) and Pparα (peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha). (C–D) Trypsin (10 nM) induces phospho-Jnk1/2 signaling in HuH7 hepatoma cells, which is suppressed by the Gi inhibitor, pertussis toxin (PTX); 15 min time-point used in D. (E) Par2 siRNA (500 nM) knockdown inhibits trypsin-induced phosphorylation of Jnk1/2 (15 min) in HuH7 cells. Trypsin induces nuclear translocation of SREBP-1c, which is inhibited by siPAR2 and by the Jnk1/2 inhibitor SP600125. β-actin and Lamin A were used as loading controls for whole cell and nuclear lysate western blots, respectively. (F) Mechanism of PAR2-Gi regulation of lipid metabolism in hepatocytes by activating Jnk1/2 and SREBP-1c pathways. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post-hoc test (A) or unpaired 2-tailed T-test (B) was performed, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, #P = 0.06.