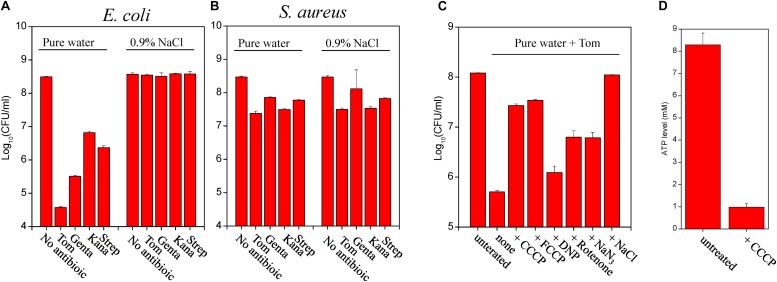
FIGURE 3.
Starvation induces formation of E. coli stationary-phase persister cells that can be eradicated by aminoglycosides upon hypoionic shock. (A,B) Survival of starvation-induced E. coli (A) and S. aureus (B) persisters following a 3-min treatment with the indicated aminoglycoside antibiotics dissolved in pure water (i.e., cells in hypoionic shock) or in a 0.9% NaCl solution. E. coli and S. aureus stationary-phase cells grown in MHB medium were resuspended in M9 medium and YNB medium (without amino acids), respectively, at a final cell density of 108 CFU/mL and agitated for 5 h prior to antibiotic treatment. Tom and Genta: 50 μg/mL; Kana: 100 μg/mL; and Strep: 200 μg/mL. (C) Survival of starvation-induced E. coli persisters following a 3-min treatment with Tom dissolved in pure water. Cells were pretreated using the same experimental conditions described in Figure 2B. (D) ATP levels in nutrient shift-induced E. coli persisters before and after CCCP treatment. Data in Panels (A–D) represent means ± SD of three replicates; independent experiments were repeated at least three times.