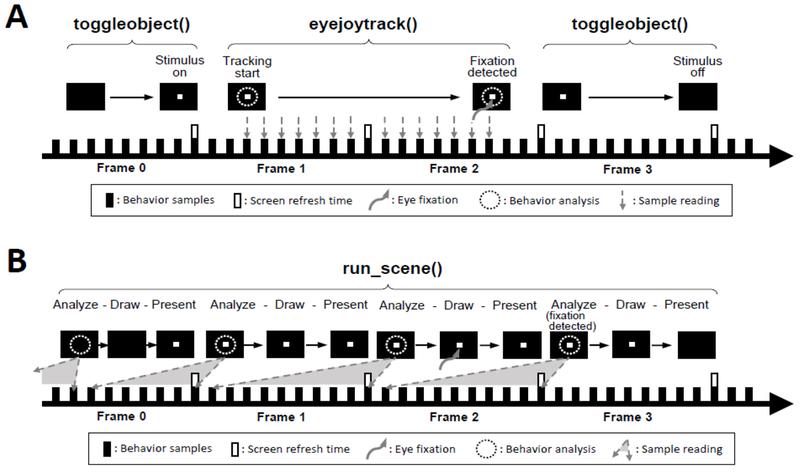
Figure 1.
Detection of eye fixation in the previous scripting method and the scene framework. A. In the previous scripting method, the stimulus (fixation point) is turned on and off by toggleobject() and the target behavior (eye fixation) is monitored by eyejoytrack(). During eyejoytrack(), behavior samples are checked every millisecond. eyejoytrack() ends as soon as the fixation is detected, but the fixation point may not be turned off until the end of the next frame. B. In the scene framework, the presentation of the fixation point and the detection of eye fixation are processed in parallel by run_scene(). run_scene() repeats a cycle of analyzing behavior samples, drawing visual stimuli on a background buffer and presenting the buffer every frame. All the samples collected during the previous frame are analyzed together at the beginning of each frame. Therefore, the occurrence of the fixation may not be known until the next frame, although the time of the fixation can still be calculated online accurately.