1.
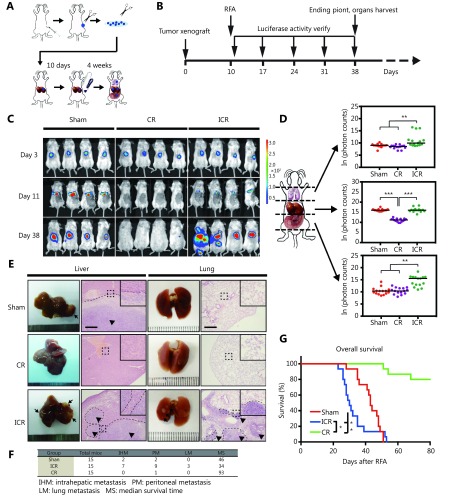
Incomplete ablation induces CRLMs recurrence in vivo. (A, B) Schematic outline of the xenograft model used in our study. Tumor pieces of equal volume (1 mm3) from the CT-26 subcutaneous xenograft tumor were transplanted into the livers of BALB/c mice. Ten days after orthotopic implantation, RFA was performed. Four weeks later, mice were killed and then their liver and lung tissues were harvested and analysed by histology or gene and protein expression. (C) Representative luminescence images and paired organs (lung and liver) from each group. ICR, incomplete RFA; CR, complete RFA. (D) Luminescence was determined in three positions (lung/upper part, liver/middle part and PM/lower part) by the schematic shown (left). The base e logarithm of the luminescence value from three groups was shown in the graft (right). P values were determined by ANOVA test. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01. (E) Representative lung and liver H&E stained histology samples (100 ×). Arrows indicate metastatic lesions. (F) Information about three groups was listed. IHM, intrahepatic metastasis; PM, peritoneal metastasis; LM, lung matastasis; MS, median survival time. (G) Kaplan-Meier overall survival curve in the xenograft mouse model suffered with RFA treatment ( n = 15 in each group). P values were determined by log-rank test. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01.