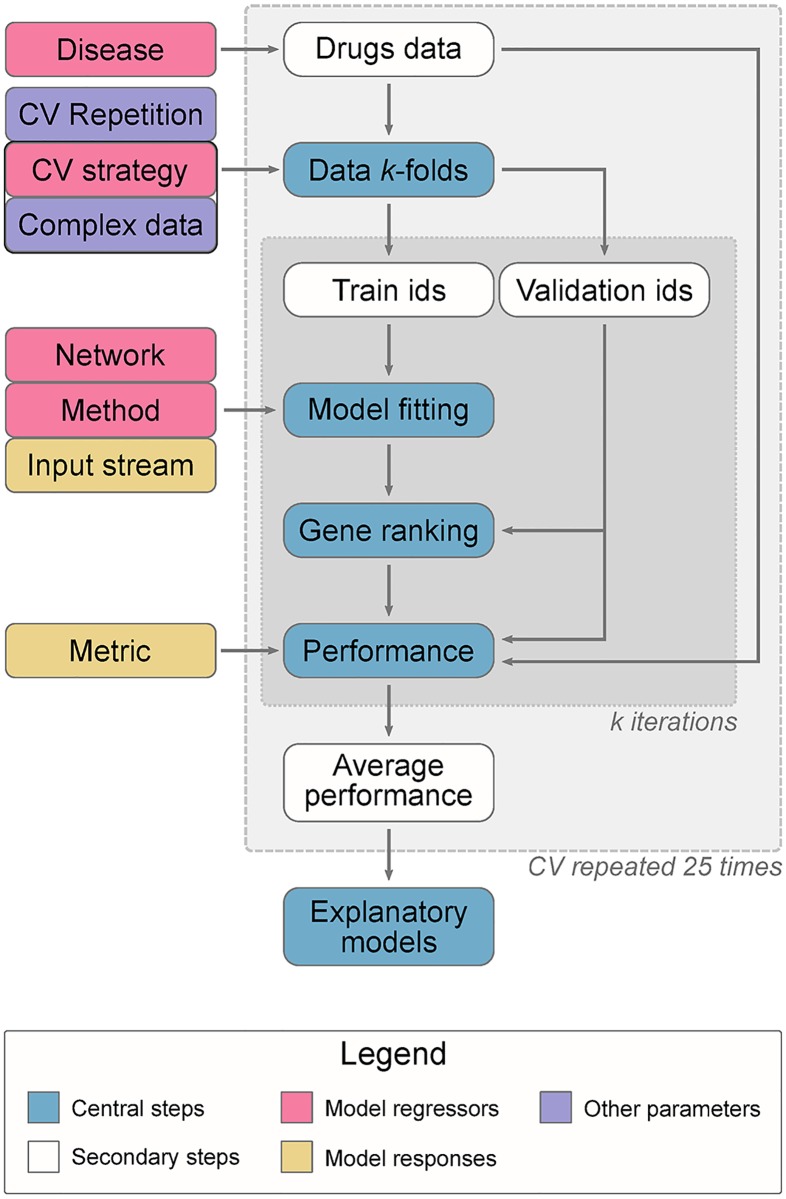
Fig 1. Benchmark overview.
This work describes six performance metrics using two input streams (genetic association and drug-based genes) to predict drug target-based genes for 22 common diseases. 3-fold cross-validation (CV), repeated 25 times, was run under three CV strategies. The gene identifiers in each fold are determined using only the drugs data, regardless of the input. Two validation strategies are complex-aware and therefore needed this data to define the splits. 15 methods based on network propagation (including 4 baselines) were evaluated, using two networks with different properties, by modelling their performance -averaged on every CV round- with explanatory models. After obtaining the performance metrics, the explanatory models allowed hypothesis testing and a direct performance comparison between diseases, CV strategies, networks and methods, by setting them as the independent variables of the models. The latter is depicted by pink (independent variables) and yellow (dependent variable) blocks, and should not be confused with the “model fitting” block, which refers to the network propagation prioritisers.