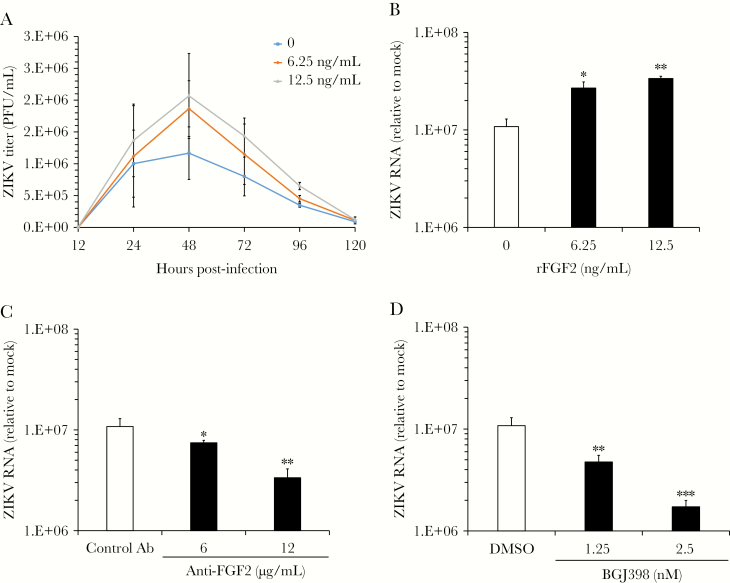
Figure 2.
Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) enhances viral replication in human fetal astrocytes (HFAs). HFAs were pretreated for 24 hours with or without recombinant human FGF2 (6.25–12.5 ng/mL) and then infected with Zika virus (ZIKV) strain PLCal (multiplicity of infection, 3). A, Medium was collected daily from infected HFAs cultured with or without FGF2, and viral titers were determined by a plaque assay. B, Total RNA was extracted 2 days after infection from HFAs and then subjected to quantitative reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis to determine how FGF2 affected levels of viral RNA. C and D, ZIKV-infected HFAs were cultured in the presence of a neutralizing mouse anti-FGF2 antibody (Ab) or an isotype-matched mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG; C) or the FGF receptor inhibitor BGJ398 or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO; D) for 2 days, after which total RNA was extracted and viral RNA quantitated by qRT-PCR. Values are expressed as the mean of 3 independent experiments. Error bars represent standard errors of the mean. PFU, plaque-forming units. *P < .05, **P < .01, and ***P < .001, by the Student t test.