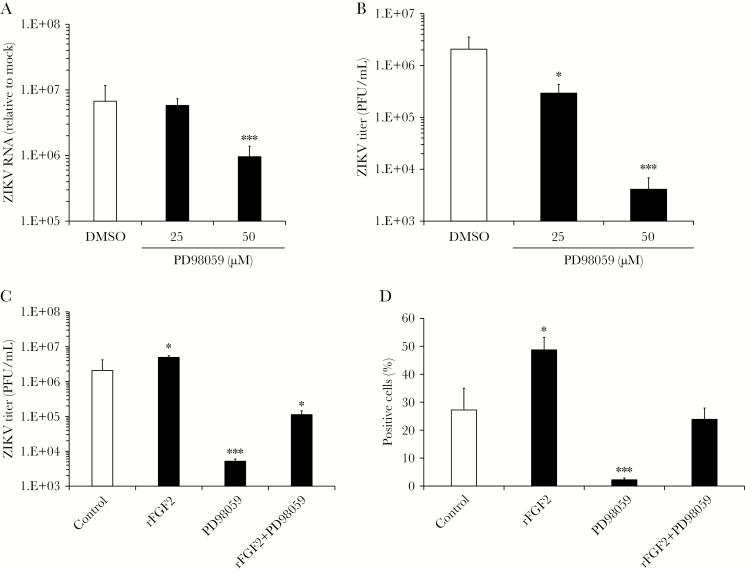
Figure 4.
MEK-1 activity is important for Zika virus (ZIKV) replication and infectivity. Human fetal astrocytes (HFAs) were infected with ZIKV strain PRVABC-59 (multiplicity of infection [MOI], 0.3) in the presence of the MEK inhibitor PD98059 or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Two days after infection, total RNA extracted from cells and supernatants were subjected to quantitative reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction analysis (A) and plaque assays (B), respectively. The effects of PD98059 (50 µM) on production of ZIKV progeny virions (C) and spread (D) were assessed in the presence and absence of recombinant human fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2; 12 ng/mL) 2 days after infection. D, Automated high-content immunofluorescence imaging was used to determine the numbers of cells positive for ZIKV E protein. Values are expressed as the mean of 3 independent experiments. Error bars represent standard errors of the mean. PFU, plaque-forming units. *P < .05 and ***P < .001, by the Student t test.