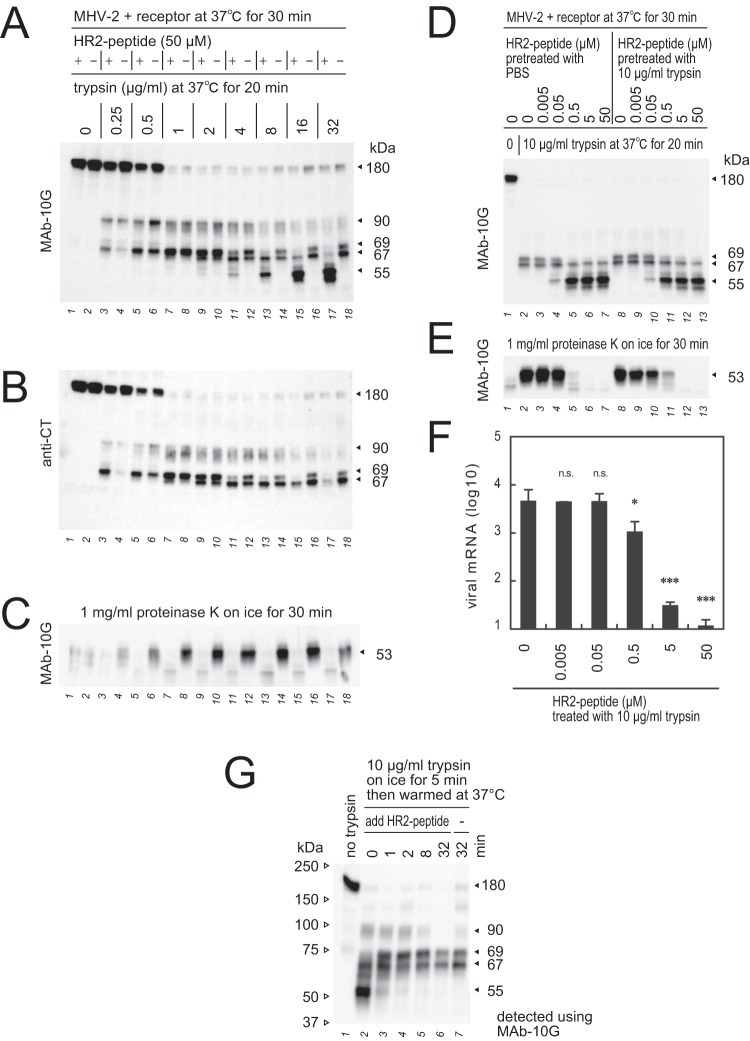
FIG 8.
Interaction of HR2-mimicking peptide with the S2 subunit. (A) Effect of HR2-mimicking peptide (HR2-peptide) during S protein triggering. HR2-peptide (50 μM) was added to MHV-2 after the receptor-binding step, and reaction mixtures were treated with various concentrations of trypsin. (B) The polyvinylidene difluoride membrane from panel A was reprobed with anti-CT antibody. (C) Reaction mixtures from panel A were treated with proteinase K to generate the 53-kDa fragment. (D) Effect of trypsin on the HR2-peptide. HR2-peptide nontreated or pretreated with 10 μg/ml trypsin for 30 min was diluted and added to the reaction mixture containing MHV-2 and receptor, and reaction mixtures were treated with 10 μg/ml trypsin. (E) Reaction mixtures from panel D were treated with proteinase K to generate the 53-kDa fragment. (F) Blocking virus cell entry. MHV-2 was adsorbed onto DBT cells, and 10 μg/ml trypsin was added in the presence or absence of HR2-peptide. After 5 h of incubation, viral mRNA was quantified by real-time PCR (n = 6). Data were analyzed relative to the no-peptide control using two-tailed Student t tests, as described in the legend of Fig. 1. (G) Time course of HR1/HR2 motif packing. During S protein activation by receptor and trypsin, the reaction was stopped by freezing at the indicated time points, and HR2-peptide was added, followed by incubation for 20 min to facilitate the formation of 67- and 69-kDa fragments. For panels A to E and panel G, Western blot analysis was performed using the indicated antibodies.