FIG 1.
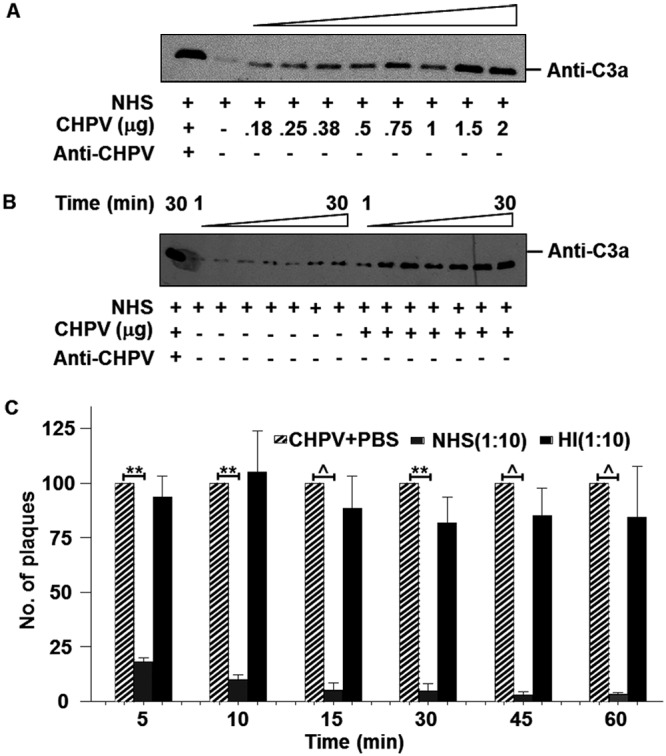
Chandipura virus is a potent activator of human complement, resulting in virus neutralization. (A) Various concentrations of CHPV as indicated were incubated with NHS (1:10 dilution) for 15 min followed by Western blotting to detect C3a, the activation product of C3. Positive control included NHS incubated with both CHPV and anti-CHPV antibody for 15 min, while the serum by itself was used to detect background levels of C3a. (B) Time course experiment was carried out by incubating CHPV with NHS for various time points as depicted followed by Western blotting to detect C3a. Serum-only samples incubated for the respective time points served as the control. (C) Effect of NHS on CHPV was determined by incubating 100 PFU of the virus with either NHS (gray bars) or heat-inactivated NHS (black bars) at a dilution of 1:10 for the respective time periods, and the remaining infectious virus was determined by plaque assays. Plaque reduction was compared against virus-only samples (hatched bars), with each bar representing 6 independent experiments. Differences in neutralization between CHPV+PBS and CHPV+NHS were found to be statistically significant with P values of ≤0.001 (**) and ≤0.0001 (^).
