Fig. 4. Wireless and battery-free UV monitoring patch.
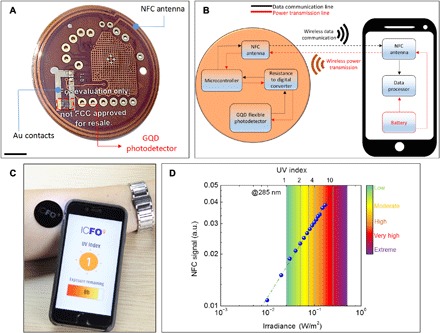
(A) Photograph of the GQD-UV patch. GQD assembly was heterogeneously integrated onto a commercially available NFC patch (TIDM-RF430-TEMPSENSE, Texas Instruments), and the electrical connection between PD and the chip is obtained by deposited metal lines. Scale bar, 10 mm. (B) Block diagram of the wireless and battery-free UV monitoring system. NFC provides two-way communication by inductively powering the patch and wirelessly sending the data to smartphone. (C) Mobile UV index monitoring via UV patch placed on the arm. The patch uses a flexible short-pass filter on the front side that blocks the wavelengths greater than 400 nm, allowing an accurate monitoring of the environmental UV index. The developed software displays the actual UV index and informs the user about recommended remaining exposure time. (D) Modulation of output NFC signal with respect to irradiance at 285 nm. High sensitivity of 1 mW/m2 allow accurate and wireless UV index measurement. The color scale shows the severity of the UV exposure according to the Diffey weighted average. Photo credit: Alina Hirschmann, ICFO-Institut de Ciencies Fotoniques.
