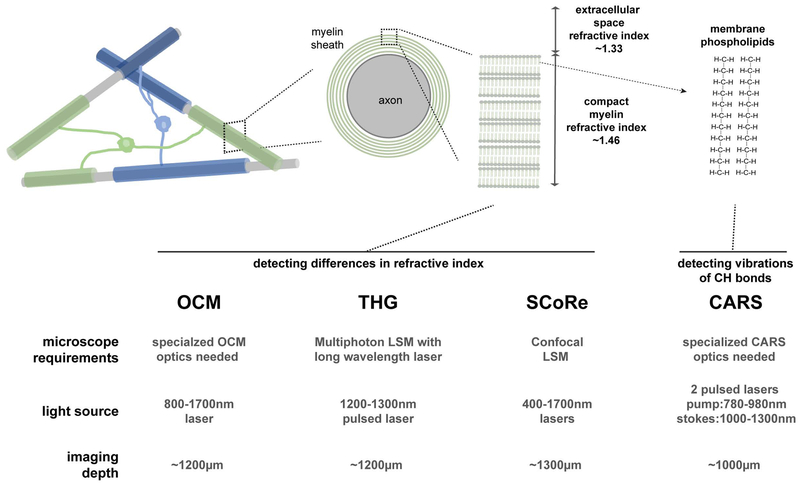
Figure 1: Approaches for label-free myelin imaging.
The myelin sheath is a unique biological structure composed of multiple layers of oligodendrocyte cell membrane wrapped tightly around single axons with very little to no cell cytoplasm between the myelin layers. The differential refractive index of the compact myelin sheath compared to the rest of the brain tissue and the high concentration of phospholipids allows label-free detection of myelin using various optical imaging approaches. These approaches include optical coherence microscopy (OCM), third harmonic generation (THG) microscopy, spectral confocal reflectance (SCoRe) microscopy, coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS) microscopy. OCM, THG and CARS require relatively complex instrumentation/light sources while SCoRe can be conducted on conventional confocal laser scanning microscopes (LSMs). Recent advances in each technique using long wavelength light sources (1300–1700nm) have achieved imaging depths above 1mm, potentially allowing intravital imaging of white matter tracts such as the corpus callosum in murine models.