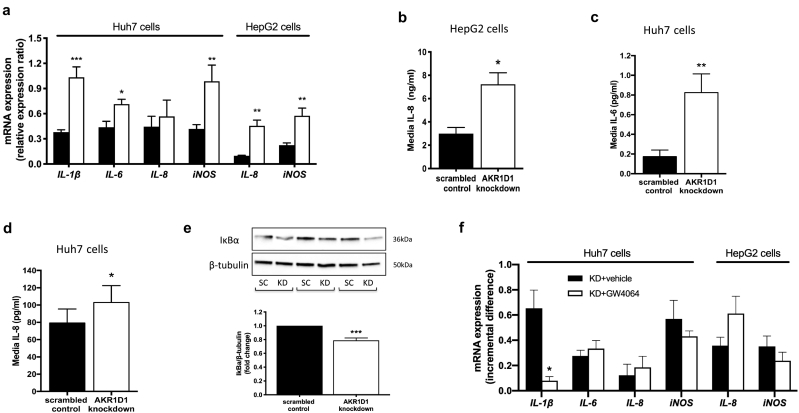
Fig. 7.
Inflammatory response in human hepatoma cell lines, following AKR1D1 knockdown. AKR1D1 knockdown (white bars) increased the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8 as did the expression of iNOS in Huh7 and HepG2 cells, as measured by qPCR (a). AKR1D1 knockdown increased the cell media concentrations of IL-8 in HepG2 cells (b), as well as of IL-6 and IL-8 cell media levels in Huh7 cells (c and d). In addition, AKR1D1 knockdown decreased the protein expression levels of IκBα, the endogenous inhibitor of NF-κB, which co-ordinates the cellular inflammatory response (e). Pharmacological manipulation of the bile acid receptor FXR, using the FXR agonist GW4064 (5 μM, 24 h), normalised the expression of IL-1β in Huh7 cells, only, whilst it had no effect on the expression of IL-6, IL-8 or iNOS in either Huh7 or HepG2 cells (f). qPCR data were normalised to 18SrRNA, protein levels were normalised to β-tubulin and cell media levels were corrected to total protein. Representative Western blot images are shown from 3 biological replicates, however formal quantification was performed in n = 7–9 replicates. Data are presented as mean ± se of n = 5–8 experiments, performed in triplicate, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, compared to scrambled controls (black bars).