Fig. 5.
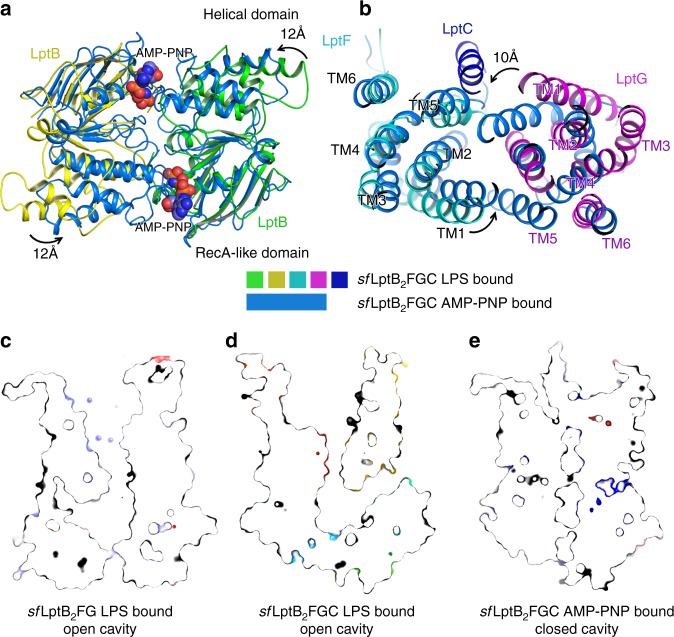
Superimpositions of AMP-PNP and LPS-bound sfLptB2FGC structures. a AMP-PNP binding induces the conformational changes of LptB (NDBs). The helical domains of the dimeric LptB (AMP-PNP-bound sfLptB2FGC) showed a rotational shift of ~12 Å in the anti-clockwise direction from the nucleotide-free state of dimeric LptB (LPS-bound sfLptB2FGC). The LPS-bound sfLptB2FGC is coloured in the same as Fig. 1. The AMP-PNP-bound sfLptB2FGC is coloured in marine blue and AMP-PNP shows as spheres. b A top view of superimposed transmembrane helices of LPS-bound sfLptB2FGC and AMP-PNP-bound sfLptB2FGC complex. AMP-PNP binding induces the TM helices of AMP-PNP-bound sfLptB2FGC to rotate in the anti-clockwise direction with the largest shift of ~10 Å from the nucleotide-free state (LPS-bound sfLptB2FGC) towards the central channel. c Slab view of surface representation of cavity of LPS-bound sfLptB2FG. The cavity is in an outward open conformation. d Slab view of cavity of LPS-bound sfLptB2FGC. The cavity is in an outward open conformation. The transmembrane helix of LptC is located at the lateral gate TM1G/TM5F, enlarging the cavity. The neck of the cavity is widely open. e Slab view of cavity of AMP-PNP-bound sfLptB2FGC. The cavity is closed, which is induced by AMP-PNP binding