Fig. 1.
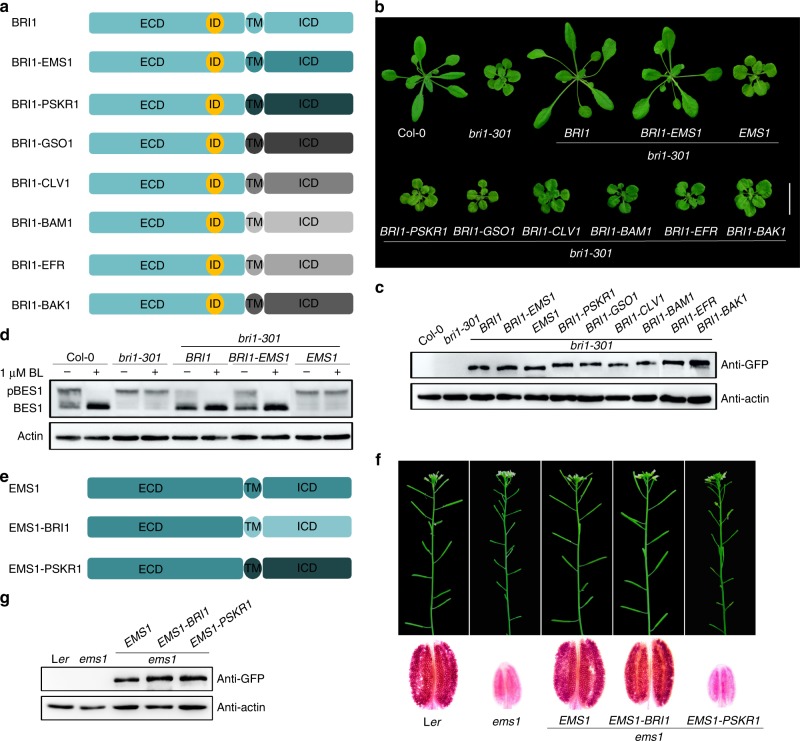
The intracellular domains of EMS1 and BRI1 are interchangeable. a Schematic diagram of the extracellular domain of BRI1 fused with the transmembrane domains and intracellular kinase domains of several LRR-RLKs that were labeled in different colors, respectively. b Phenotypes of 4-week-old transgenic lines expressing BRI1, BRI1-EMS1, EMS1, BRI1-PSKR1, BRI1-GSO1, BRI1-CLV1, BRI1-BAM1, BRI1-EFR and BRI1-BAK1 under the BRI1 promoter in bri1-301 background. Scale bar, 2.0 cm. c Protein expression levels of the transgenes with GFP tag in the rosette leaves of the corresponding plants shown in b were detected with anti-GFP antibody. Actin served as the loading control. d Phosphorylated BES1 (pBES1) and dephosphorylated BES1 were detected with BES1 antibodies in the extracts of 10-day-old seedlings of the indicated genotypes. Where indicated, the plants were treated with 1 μM BL for 1 h before preparation of the extracts. Actin served as the loading control. e Schematic diagram of chimeric receptor kinases EMS1-BRI1, EMS1-PSKR1. The EMS1, BRI1 and PSKR1 protein structures were labeled in blue, light blue and dark blue, respectively. f Phenotypes of 6-week-old transgenic lines expressing EMS1, EMS1-BRI1, EMS1-PSKR1 under the EMS1 promoter in ems1. Primary inflorescences (top) and Alexander staining of pollen grains in mature anthers (bottom) showing the fertility phenotypes of the transgenic plants. g Protein expression levels of the transgenes with GFP tag in the inflorescences of the corresponding plants shown in f were detected with anti-GFP antibody. Actin served as the loading control