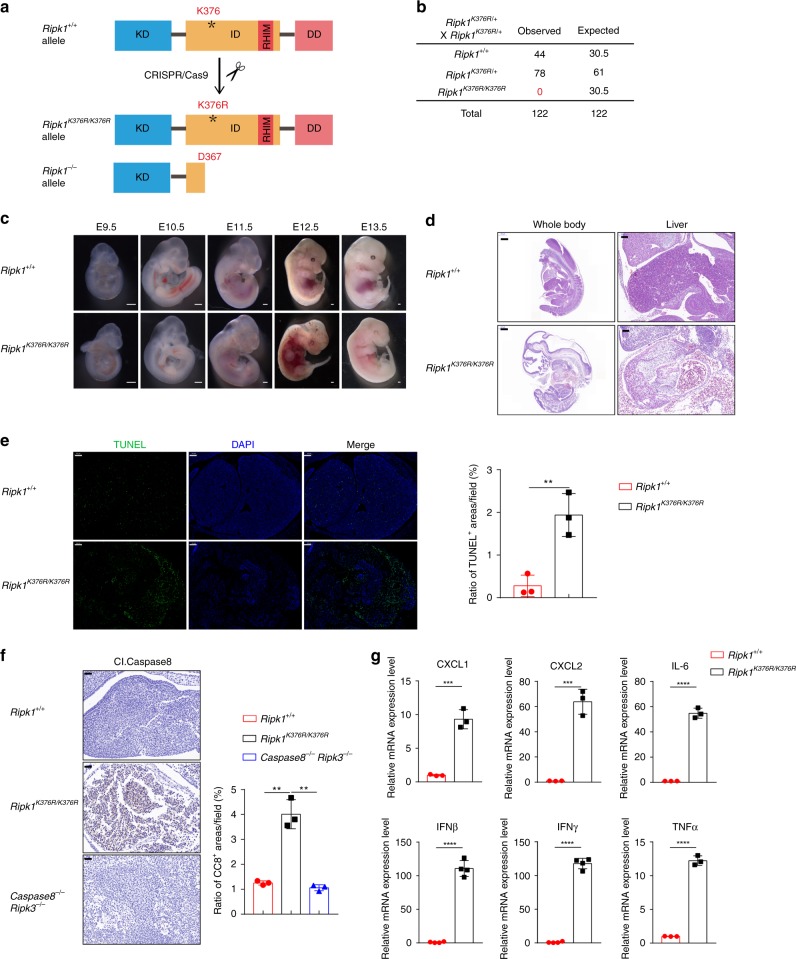
Fig. 1.
Ripk1K376R/K376R mutation results in embryonic lethality. a Schematic overview of strategy to generate Ripk1K376R/K376R and Ripk1−/− mice by CRISPR-Cas9 technology. KD, kinase domain; ID, intermediate domain; DD, death domain; RHIM, RIP homotypic interaction motif. b Statistical analysis of the expected and observed offspring mice (1-month-old) from the intercrosses of Ripk1K376R/+ mice. c The representative images of embryos with the indicated genotypes from E9.5 to E13.5 (scale bar, 1 μm). d Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of embryos (left, scale bar, 500 μm) and liver sections (right, scale bar, 100 μm) at E12.5. e Microscopic images and statistical results of TUNEL staining in liver sections at E12.5 (scale bar, 100 μm; Ripk1+/+ embryo, n = 3; Ripk1K376R/K376R embryo, n = 3). f Microscopic images and statistical results of three different area of cleaved Caspase8 staining of embryos at E12.5 (scale bar, 50 μm; Ripk1+/+ embryo: n = 3; Ripk1K376R/K376R embryo: n = 3; Ripk3−/−Caspase8−/− embryo: n = 3). g qRT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines expression in embryo homogenates at E12.5. Data are mean ± s.e.m. (Ripk1+/+ embryo: n = 3; Ripk1K376R/K376R embryo: n = 3). Statistical significance was determined using a two-tailed unpaired t test, **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001