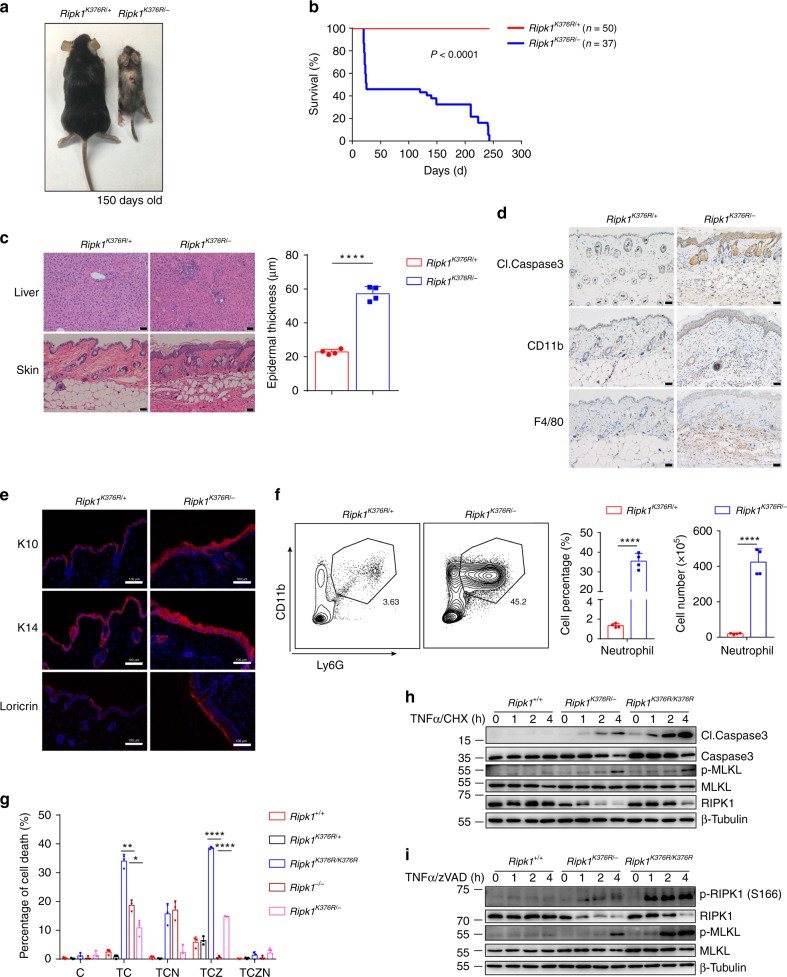
Fig. 6.
Ripk1K376R/− mice develops spontaneous inflammation. a Representative macroscopic images of Ripk1K376R/− and Ripk1K376R/+ littermate mice at P150. b Survival curves of Ripk1K376R/− and Ripk1K376R/+ mice. c H&E staining of liver and skin sections of Ripk1K376R/− and Ripk1K376R/+ littermate mice at P150 (scale bar, 50 μm), and microscopic quantification of the epidermal thickness from H&E results (Ripk1K376R/+ mice: n = 4; Ripk1K376R/− mice: n = 4). d, e Immunohistochemical staining of cleaved Caspase3, CD11b, and F4/80 (scale bar, 50 μm) (d) or immunofluorescence staining of Loricrin, K10, and K14 (scale bar, 100 μm) (e) in skin sections of Ripk1K376R/− and Ripk1K376R/+ littermate mice at P150. f Flow cytometry and statistical results of splenocytes stained with Ly6G and CD11b from Ripk1K376R/− and Ripk1K376R/+ littermate mice at P150 (Ripk1K376R/+ mice: n = 4; Ripk1K376R/− mice: n = 4). CD11b+Ly6G+ cells were identified as neutrophils. g Cell death of Ripk1+/+, Ripk1K376R/+, Ripk1K376R/K376R, Ripk1−/−, and Ripk1K376R/− immortalized MEFs treated for 5 h with different stimulators was measured by SytoxGreen positivity. The error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. of data from three independent cell samples for each genotype. T: TNFα; C: cycloheximide (CHX); Z: zVAD.fmk; N: necrostatin-1. h, i Ripk1+/+, Ripk1K376R/K376R, and Ripk1K376R/− immortalized MEFs were treated with TNFα/CHX (h) or TNFα/ zVAD.fmk (i) for the indicated time, and the cell lysates were analyzed by western blotting using the indicated antibodies. In g–i, TNFα, 20 ng/ml; CHX: 10 μg/ml; zVAD.fmk, 20 μM; necrostatin-1, 10 μM. In c, f, g, data are mean ± s.e.m. Statistical significance was determined using a two-tailed unpaired t test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ****P < 0.0001