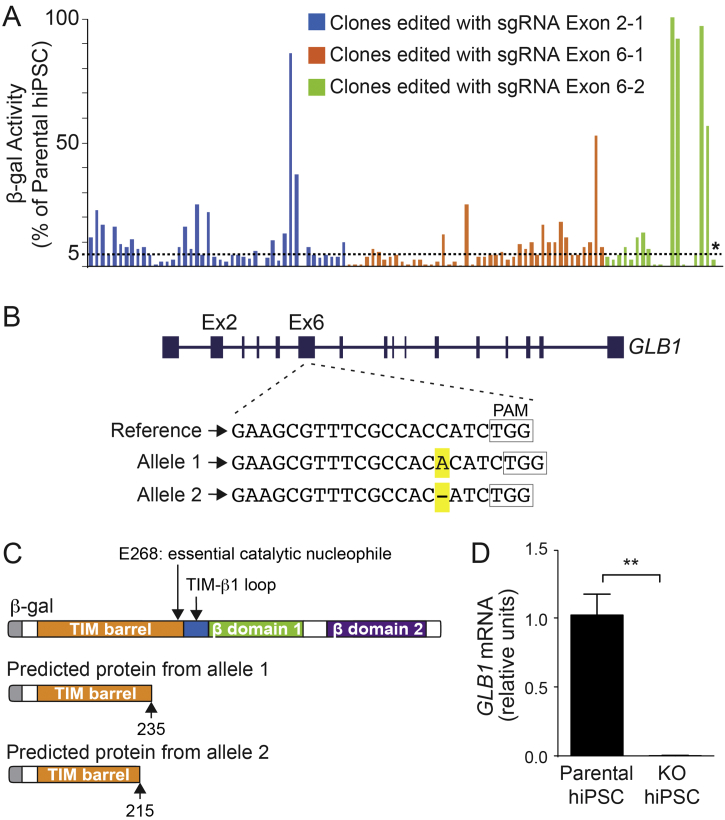
Fig. 1.
GLB1 knockout clone screening and mutation confirmation.
(A) Screening of CRISPR/Cas9-edited clones using a β-gal enzyme activity assay. Three different sgRNAs, one targeting exon 2 (Exon 2-2) and two targeting exon 6 (Exon 6-1 and Exon 6-2), were designed and used for editing the GBL1 gene in hiPSCs. The resulting 107 colonies were screened for β-gal enzyme activity and plotted: 44 for sgRNA Exon 2-1 (blue bars), 44 for sgRNA Exon 6-1 (orange bars) and 19 for sgRNA Exon 6-2 (green bars). Of those, two clones produced by each sgRNA, with undifferentiated morphology and <5% enzyme activity (compared with the parental cell line [value set at 100%]) were sequenced. An asterisk marks the clone selected for further experiments. (B) Characterization of the mutations in the selected knockout hiPSC clone. The reference sequence of the GLB1 gene in the edited region is shown. Allele 1 contains a 1 base-pair insertion, an A, and allele 2 contains a 1 base-pair deletion, both highlighted in yellow. Boxes outline the location of the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence. (C) Predicted proteins resulting from the mutations in alleles 1 and 2 compared with β-gal protein domains(top;, adapted from [48]). Both mutations are predicted to produce truncated proteins prior to E368, an important catalytic nucleophile. (D) Relative mRNA expression of GLB1 normalized to GAPDH. KO, GBL1 knockout organoids. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation (SD), n = 3 for each line) (⁎⁎p < .01, t-test analysis between control and KO values). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)