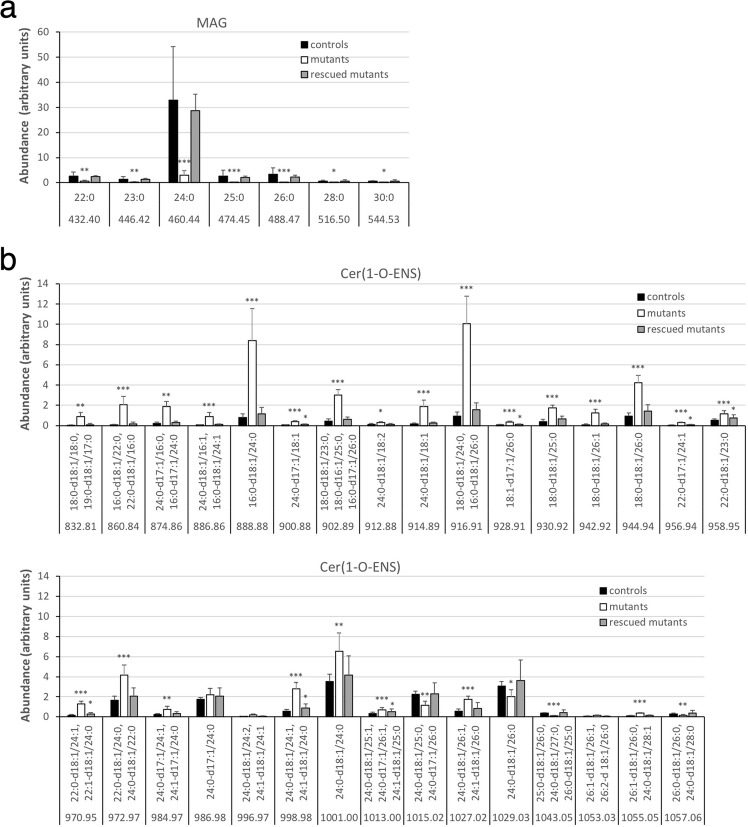
Figure 8.
Alterations in MAG and 1-O-acylceramide content in unbound epidermal lipids in Fatp4−/− mice. Fractions 3 and 2 of unbound epidermal lipids of newborn mice were analyzed by ESI-MS in the positive-ion mode as [M + NH4]+ ions (a) and as [M + H]+ ions (b), respectively, and quantified in arbitrary units. The decreased levels of MAG species seen in Fatp4−/− mice were all normalized by the Fatp1 transgene (a). Fatp4−/− mice showed increased levels of many Cer(1-O-ENS) species that carried 48 or fewer total carbons in their two acyl chains, almost all of which were normalized by the Fatp1 transgene (b). Data were obtained from 4 each of Fatp4+/− (controls), Fatp4−/−, and FATP1-rescued mutants with m/z ratios, standard deviation, and statistical significance shown (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001). See Materials and Methods for nomenclature. MAG species are listed by their acyl groups. Cer(1-O-ENS) species at the same m/z ratio are listed in descending order in amount found in controls.