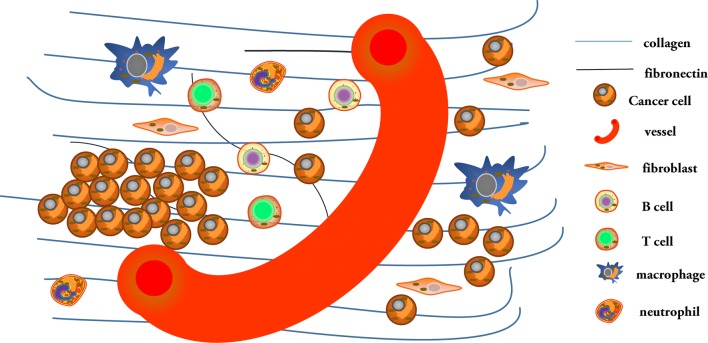
Fig. 2.
The complexity between collagen and the extracellular matrix. Multiple stromal cells and the extracellular matrix play important roles in stimulating or inhibiting collagen functions via different pathways in cancer progression. Collagen-rich extracellular matrices can bind to other molecules to form dense fibrosis, which induces an anoxic environment and changes the condition of new blood vessels. The behavior of cancer cells is also closely related to collagen. This process also affects the activity and localization of innate and adaptive immune cells