Fig. 3.
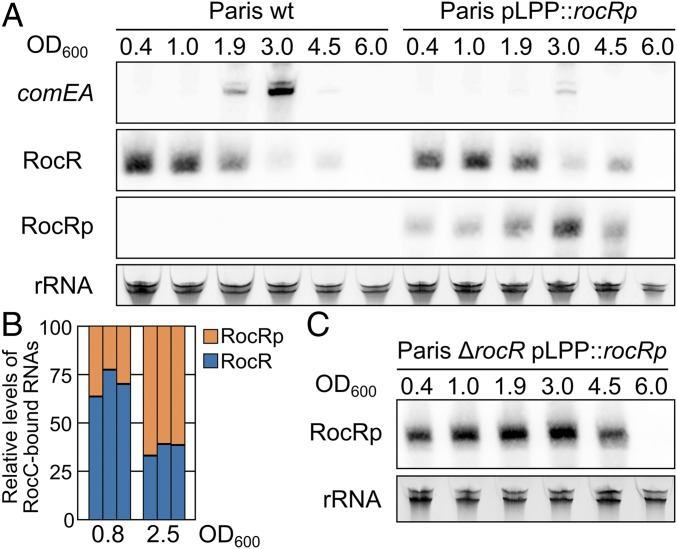
RocRp acts as a substitute for RocR. (A) Northern blot analysis of comEA mRNA, RocR, and RocRp expression during growth of the wild-type Paris strain or carrying the rocRp gene in pLPP (Paris pLPP::rocRp) in AYE medium at 30 °C. Total RNA was extracted at the indicated ODs (OD600) during the exponential growth phase (0.4 to 1.0), the transition phase (1.9 and 3.0), and the early (4.5) and late stationary phases (6.0). (B) Relative quantification of RocR and RocRp bound to RocC in the exponential phase (OD = 0.8) and transition phase (OD = 2.5). For each OD, 3 independent cultures of the strain Paris pLPP::rocRp were obtained. RNAs that copurified with RocC were reverse-transcribed with a mix of primers specific for RocR and RocRp, each bearing the same 5′ end extension. The resulting cDNAs were amplified by PCR using primers corresponding to the 5′ extension of the reverse transcription primer and a reverse primer that matches both RocR and RocRp. Amplification of either RocR or RocRp produces an 85-bp DNA. PCR products originating from RocR and RocRp were distinguished and quantified by restriction with NruI, which cuts only the RocRp PCR product into 2 fragments. (C) Northern blot analysis of RocRp expression during growth in AYE medium at 30 °C of the strain Paris pLPP::rocRp deleted of rocR. Ribosomal RNAs were used as loading controls.