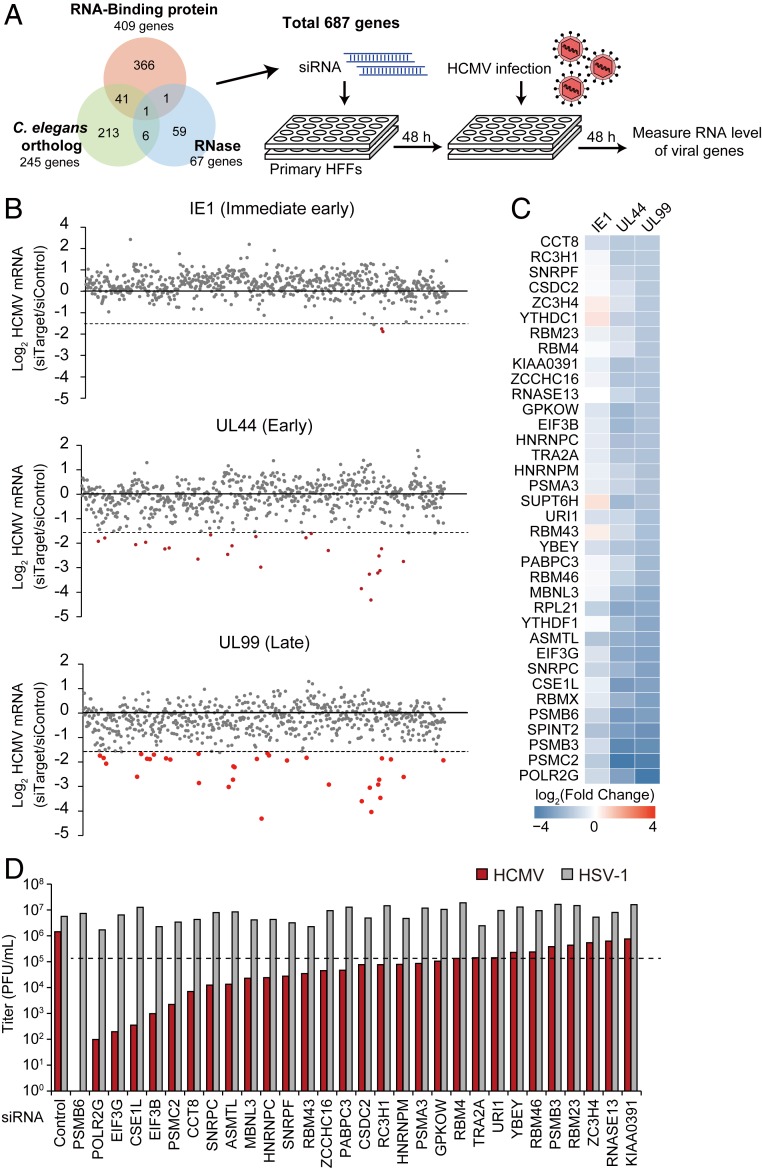
Fig. 1.
Identification of RNA-binding proteins that regulate HCMV lytic infection through siRNA screening. (A) Experimental scheme of siRNA screening. RNases, RNA-binding proteins, and orthologous genes in the small-RNA pathway from C. elegans were collected for screening. HFF cells underwent two rounds of siRNA transfection, with infection with HCMV (MOI = 2). Viral gene expression was measured by qRT-PCR at 48 hpi and normalized against GAPDH mRNA levels. (B) Summarized results of RNAi screening. IE1, UL44, and UL99 mRNA levels were quantified. Genes showing a >threefold decrease are highlighted in red. (C) Genes showing a >threefold decrease in UL99 mRNA level are selected. Heatmap of fold changes [log2(siTarget/siCon)] of viral mRNA levels in cells depleted of each gene. (D) HCMV and HSV-1 viral replication as measured by plaque-forming assay. HFFs were infected with HCMV or HSV-1 (MOI = 0.1), and the cell-free supernatants were titrated at 7 dpi for HCMV and 2 dpi for HSV-1.